The SWOT analysis diagram in PowerPoint format includes four slides. Firstly we have the SWOT template in two formats. Secondly we present SWOT matrix in the other two formats. As the same diagram PowerPoint template series, you can also find our Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, Venn diagram, Data Mining, Machine Learning, cloud computing, Artificial Intelligence and BlockChain PowerPoint templates.
SWOT Analysis, a strategic planning tool, is utilized by businesses of all sizes and across multiple industries to assess their position in the competitive landscape. This framework aids in identifying internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats, hence, the acronym SWOT. By performing a SWOT analysis, organizations can develop strategies to leverage their strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and mitigate threats.
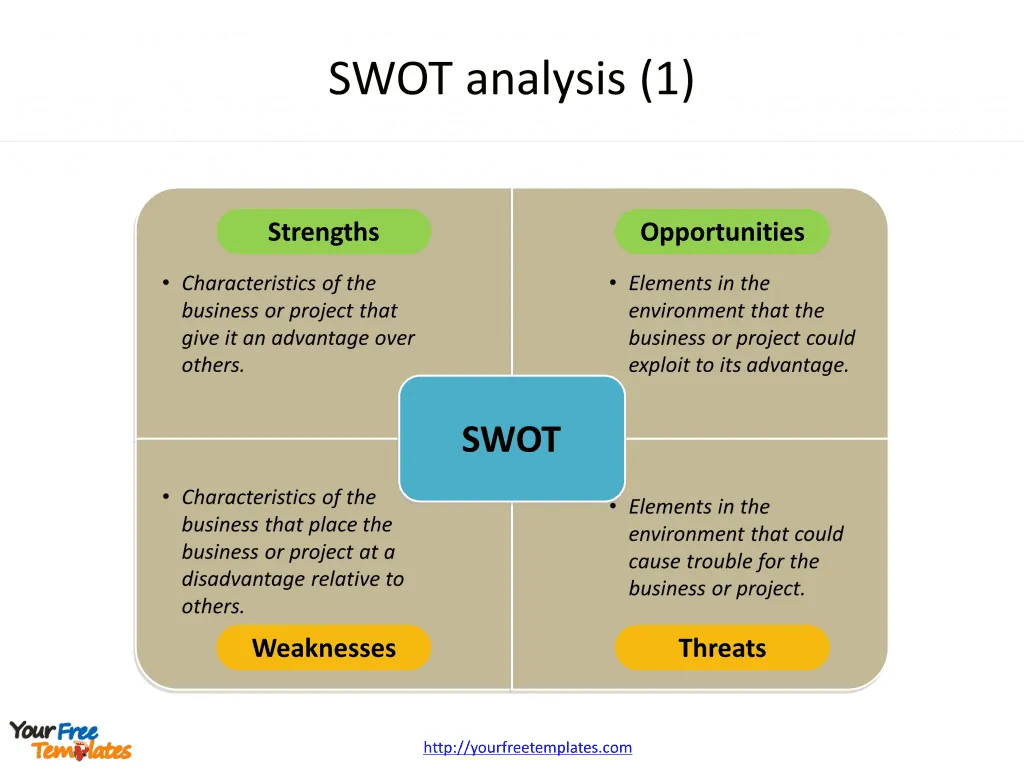
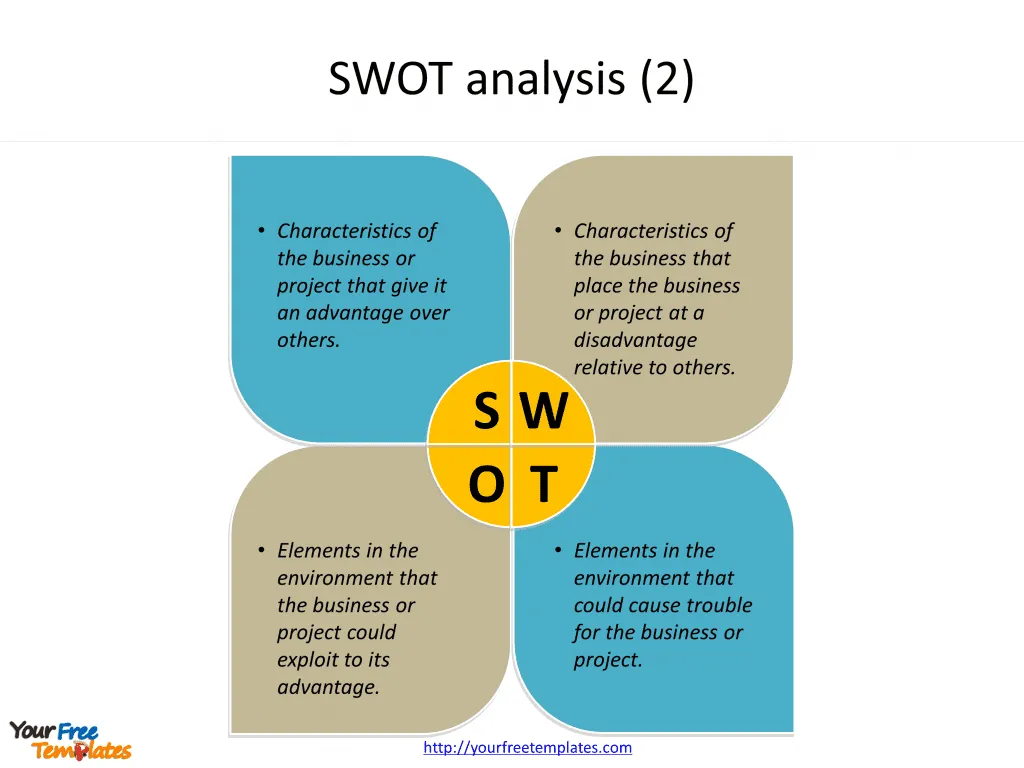
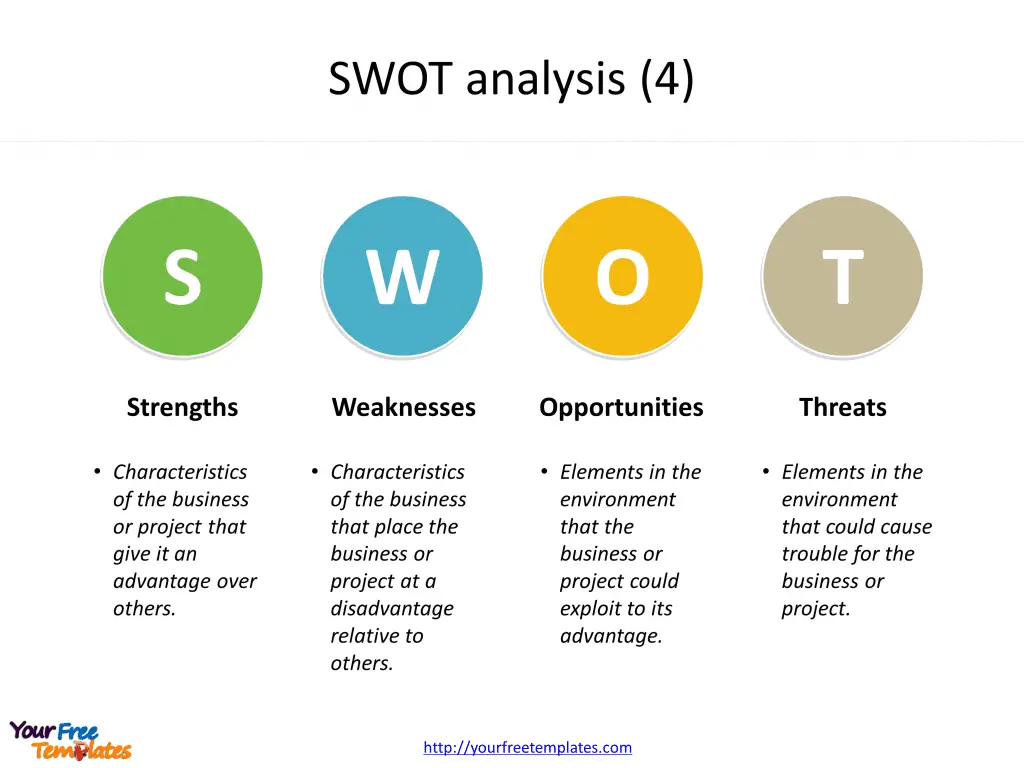
Slide 1 and 2, SWOT analysis templates.
What is a SWOT Analysis?
A SWOT analysis is a planning process that helps your company identify and understand key factors that could influence the success of a business decision or action. The SWOT acronym stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. These components represent the internal and external factors that could impact your organization’s performance and growth.
Strengths
Strengths refer to the internal attributes that give your organization an advantage over others. This could include a strong brand reputation, unique products or services, exceptional customer service, or a highly skilled team. Recognizing your strengths helps in harnessing them for maximum benefit.
Weaknesses
Weaknesses, on the other hand, represent the internal factors that could potentially hinder your progress. These could be areas where your business falls short, such as outdated processes, inadequate resources, or a weak online presence. Acknowledging these weaknesses allows you to strategize on how to overcome them.
Opportunities
Opportunities are external factors or conditions that your organization could potentially exploit for its benefit. This could include emerging markets, technological advancements, or gaps in the market that your company could fill. Recognizing and seizing these opportunities could help expand your market reach, diversify your offerings, or even venture into new territories.
Threats
Threats, like opportunities, are external factors. However, unlike opportunities, they pose challenges to your organization. Increased competition, economic volatility, regulatory changes, or changing market trends are examples of threats. Recognizing these threats helps in developing strategies to minimize their impact on your operations.
Importance of a SWOT Analysis
The SWOT analysis is a crucial step in strategic planning because it provides a comprehensive view of your organization’s current situation and potential future. It creates a space for teams to dream, evaluate, and worry before taking action, thereby turning insights into assets for creating a roadmap for a particular initiative.
Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses
A SWOT analysis helps identify the strengths and weaknesses of your organization. Strengths could be anything from having a strong brand reputation to owning proprietary technology that sets you apart from the competition. Recognizing these strengths helps in leveraging them for maximum benefit.
Weaknesses could be anything from outdated technology to inadequate resources or inefficiencies in your current processes. Acknowledging these weaknesses provides a starting point for improvements. You can establish targeted initiatives for improvement, upskill your team, adopt new technologies, and enhance your overall operational efficiency.
Recognizing Opportunities and Threats
Recognizing opportunities and threats is another crucial aspect of a SWOT analysis. Opportunities could include emerging markets, technological advancements, or gaps in the market that your company could fill. By seizing these opportunities, you can expand your market reach, diversify your product offerings, forge strategic partnerships, or even venture into untapped territories.
Threats are external factors that are beyond your control and pose challenges to your business. Increased competition, economic volatility, evolving regulatory landscapes, or even changing market trends are examples of threats. By proactively assessing and addressing them, you can develop contingency plans, adjust your strategies, and minimize their impact on your operations.
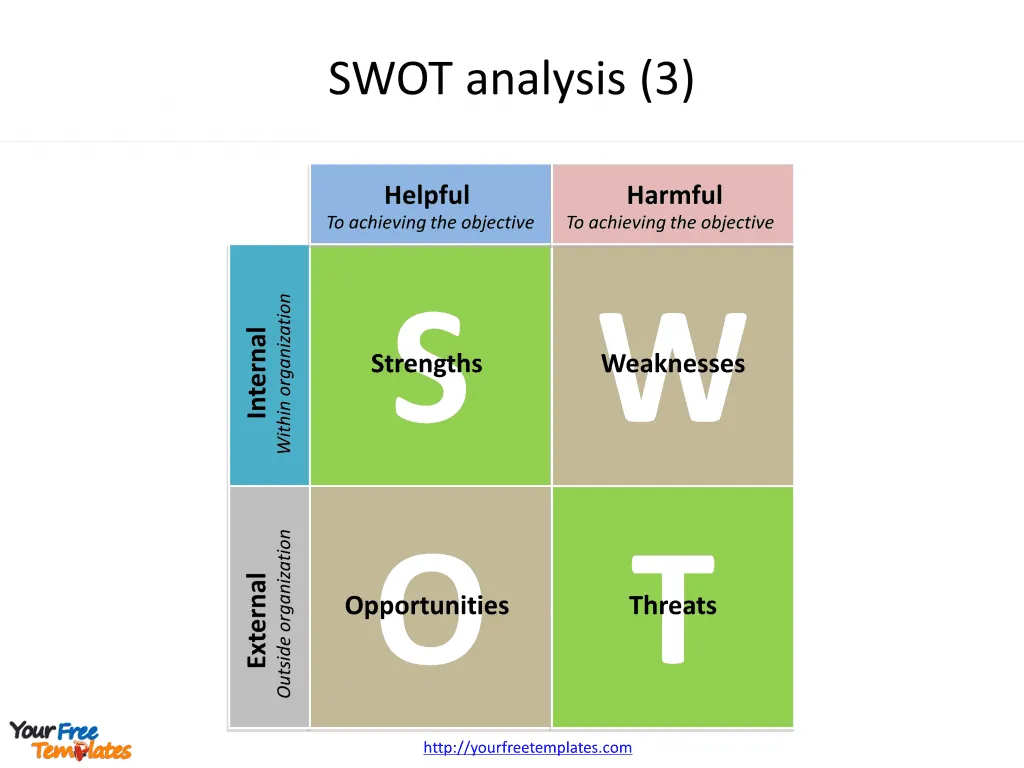
Slide 3 and 4, SWOT template.
Steps to Conduct a SWOT Analysis
Conducting a SWOT analysis requires a strategic approach. Here are some steps to guide you through the process:
-
Identify Your Objective: Determine what you want to analyze with your SWOT analysis. It could be your overall business strategy, a particular project, or even a specific campaign.
-
Identify Your Strengths: Evaluate what your organization does well. Consider what sets you apart from your competitors and why your target audience prefers your organization.
-
Identify Your Weaknesses: Analyze areas where your organization falls short. Consider what can be improved and what resources you could use to enhance your performance.
-
Consider Your Opportunities: Identify external factors that could contribute to your organization’s growth. Consider emerging markets, technological advancements, or gaps in the market that your company could fill.
-
Contemplate Your Threats: Identify external factors that could pose challenges to your organization. Consider increased competition, economic volatility, or evolving regulatory landscapes.
-
Develop an Action Plan: After conducting a SWOT analysis, develop an action plan based on the results. This plan should focus on leveraging strengths and opportunities to overcome weaknesses and threats.
SWOT Analysis Template
A SWOT analysis is often presented in a grid format, divided into four quadrants. Each quadrant represents one of the four elements. Using a SWOT analysis template can help structure the information and visualize the analysis. Here’s our simple SWOT analysis template to download and get you started:
Remember, a well-rounded SWOT analysis empowers you to capitalize on strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and navigate threats — all while making informed decisions for the future.
SWOT Analysis Examples
To help you better understand how to conduct a SWOT analysis, let’s look at a few examples:
Example 1: Apple
Strengths: Strong brand reputation, innovative products, and product inter-connectivity. Weaknesses: High prices, closed ecosystem, and lack of experimentation. Opportunities: Expand distribution options, create new product lines, and advance technology. Threats: Tough competition, lawsuits, and international issues.
Example 2: Small Restaurant
Strengths: Unique menu, excellent customer service, and loyal customers. Weaknesses: Limited seating capacity, lack of online presence, and limited marketing budget. Opportunities: Catering services, online ordering system, and partnerships with food delivery apps. Threats: Nearby competitors, changing food trends, and fluctuating food costs.
Conclusion
A SWOT analysis is a valuable tool for strategic planning. It provides a comprehensive view of your organization’s current situation and potential future. By identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, you can develop strategies that leverage strengths, improve weaknesses, seize opportunities, and mitigate threats. Remember, the key to a successful SWOT analysis lies in recognizing your organization’s strengths and weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and addressing threats head-on.
For detailed info on SWOT sample, please refer to Wikipedia.
Size:78K
Type: PPTX
Aspect Ratio: Standard 4:3
Click the blue button to download it.
Download the 4:3 Template
Aspect Ratio: Widescreen 16:9
Click the green button to download it.
Download the 16:9 Template