The Supply chain management template in PowerPoint format includes three slides. Firstly we have the slide describing SCM timeline. Secondly the PowerPoint template is for SCM Business process integration with icons. Thirdly there are nine components of SCM. As the same series, you can also find our Data Mining, Machine Learning, Block-chain technology, cloud computing and Artificial Intelligence PowerPoint templates.
Supply chain management (SCM) is a vital aspect of any business operation, playing a crucial role in the efficient movement of goods and services from the production line to the customer. In the modern business landscape, the importance and complexity of SCM have amplified, with increasing focus on not just the physical movement of goods but also data management, customer service, and profitability.
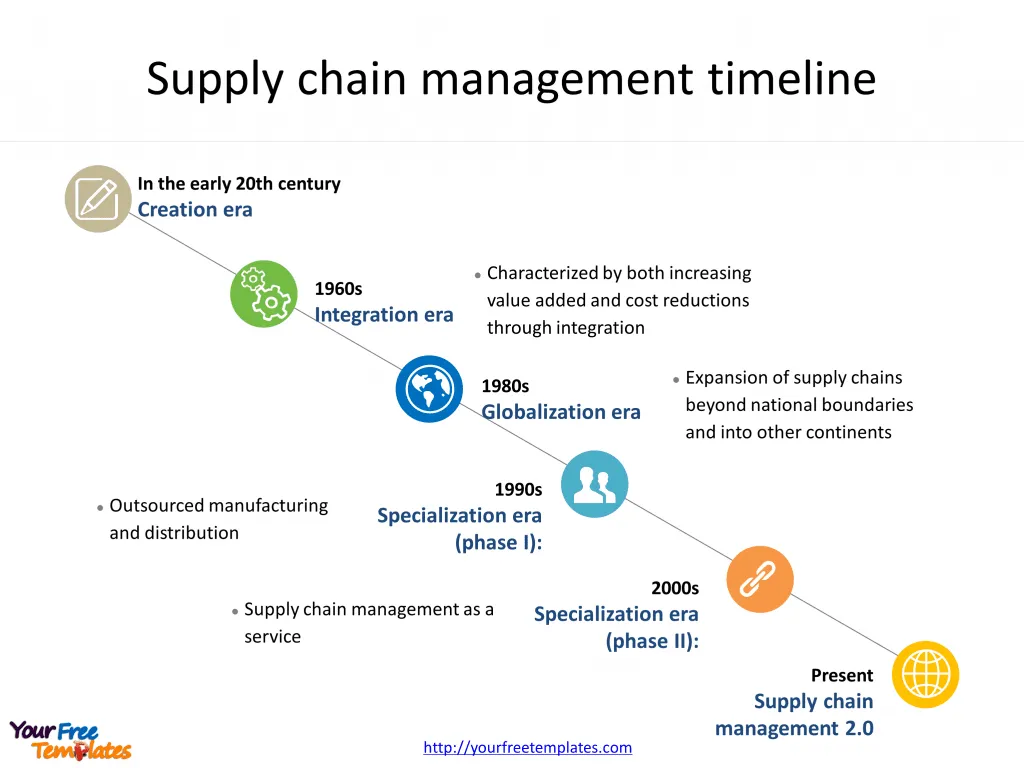
Slide 1, Supply chain management timeline
It is known that there are six stages for the development of SCM.
- First is Creation era. It is in the early 20th century, especially with the creation of the assembly line.
- Secondly is Integration era, from EDI through ERP systems.
- Thirdly is Globalization era, global systems of supplier relationships and the expansion of supply chains beyond national boundaries and into other continents.
- Fourthly and fifthly are Specialization eras, meaning outsourced manufacturing and distribution and supply chain management as a service respectively.
- Finally is SCM 2.0, describing both changes within supply chains themselves as well as the evolution of processes, methods, and tools to manage them in this new “era”. You can found them in our PowerPoint templates.
The Future of Supply Chain Management
With the advent of big data and advanced analytics, the future of supply chain management looks promising. Modern supply chains leverage the massive amounts of data generated by the chain process, curated by analytical experts and data scientists. The focus is on optimizing the usefulness of this data by analyzing it in real time with minimal latency.
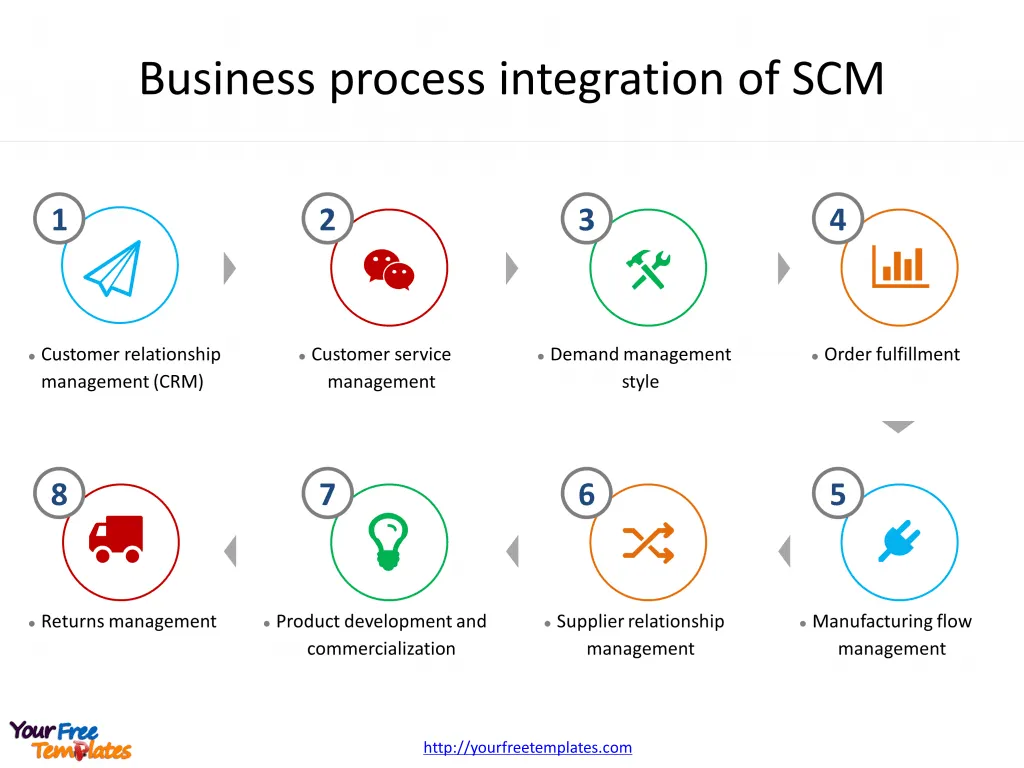
Slide 2, Business process integration of Supply Chain Management (SCM)
Phases of Supply Chain Management
An effective supply chain manager’s role extends beyond traditional logistics and purchasing. It includes finding ways to augment efficiency, minimize costs, prevent supply shortages, and prepare for unexpected contingencies.
Planning
The SCM process often commences with meticulous planning to align supply with customer and manufacturing demands. Companies strive to forecast future requirements and act accordingly. This takes into consideration the raw materials or components needed, equipment capacity, and staffing requirements.
Sourcing
Sourcing involves working with vendors to supply the materials needed throughout the manufacturing process. It entails ensuring that the raw materials meet the manufacturing specifications, the prices paid to the vendor align with market expectations, and the vendor has the flexibility to deliver emergency materials due to unforeseen events.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the core of the supply chain management process. Here, the company leverages its machinery and labor to transform raw materials into a final product. The manufacturing process may include sub-tasks such as assembly, testing, inspection, and packaging.
Delivery
Once the products are manufactured and sales are finalized, the company needs to deliver those products to its customers. Effective SCM requires robust logistic capabilities and delivery channels to ensure timely, safe, and cost-effective delivery of its products.
Returns
The SCM process concludes with support for the product and management of customer returns. The transaction with the customer must be remedied whether the company is conducting a product recall or a customer is dissatisfied with the product.
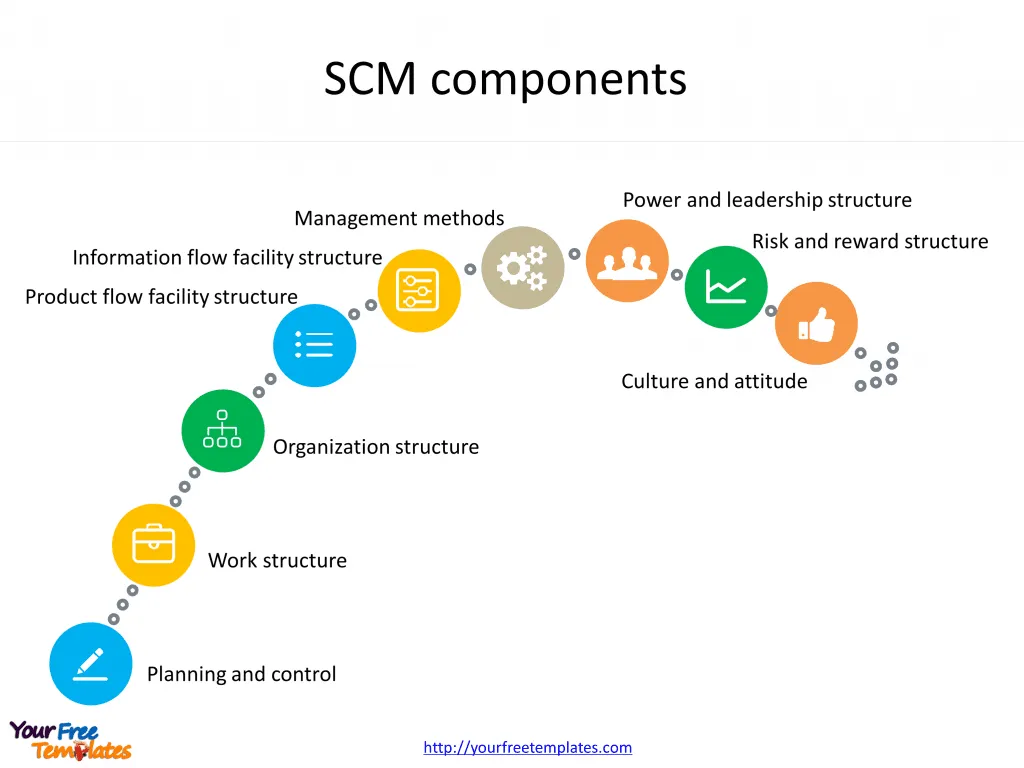
Slide 3, Supply chain management components
Then let’s discuss the components of SCM in this slide. There are nine components in SCM, which could be used by companies to acheive their differeny purposes below.
Supply Chain Models
The SCM process varies for different businesses. Each firm has its own goals, constraints, and strengths that shape its SCM efforts. Here are a few models that companies can adopt:
-
Continuous Flow Model: This model is suitable for mature industries where the manufacturer produces the same goods repeatedly, and customer demand shows little variation.
-
Agile Model: This model is ideal for companies with unpredictable demand or custom-order products. It prioritizes flexibility, allowing the company to pivot according to specific needs at any given moment.
-
Fast Model: This model emphasizes quick turnover of a product with a short life cycle. It aims to capitalize on a trend, produce goods quickly, and ensure the products are sold before the trend ends.
-
Flexible Model: This model works best for companies affected by seasonality. It ensures that production can be ramped up or wound down easily.
-
Efficient Model: For companies competing in industries with tight profit margins, making their SCM process more efficient can provide a competitive edge.
The Importance of Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management is crucial as it helps achieve several business objectives. Controlling manufacturing processes can improve product quality, reduce the risk of recalls and lawsuits, and help build a strong consumer brand. Similarly, control over shipping procedures can improve customer service by avoiding costly shortages or periods of inventory oversupply.
Meanwhile you can check detailed conception of SCM in Wikipedia.
Size:152K
Type: PPTX
Aspect Ratio: Standard 4:3
Click the blue button to download it.
Download the 4:3 Template
Aspect Ratio: Widescreen 16:9
Click the green button to download it.
Download the 16:9 Template