The Value chain Template in PowerPoint format includes three slides. Firstly we have Michael Porter’s value chain. Secondly we discover Arrow Process of value-chains. Finally is Internet of Things value-chains. As the same diagram PowerPoint template series, you can also check our Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Strategy, National Diamond, SWOT analysis PowerPoint templates.
The value chain, a concept that has been at the core of business strategy for decades, is a sequence of activities that companies go through to create and supply a product to the market. The concept was initially introduced by Michael Porter in his book Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. This article will delve deep into understanding the value chain, its components, benefits, and the process of conducting a value chain analysis.
Understanding the Concept
The value chain is a framework that dissects a business into strategically relevant activities. The goal is to understand the sources of value that a business creates at each step of its process. This value can either be in the form of higher prices realized due to superior product features or lower costs due to operational efficiencies.
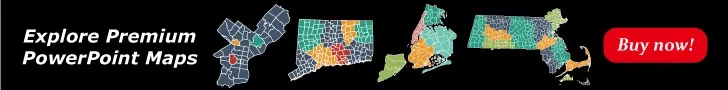
Slide 1, Michael Porter’s value chain
All five primary activities are essential in adding value and creating a competitive advantage and they are:
- Inbound logistics
- Operations
- Outbound logistics
- Marketing and sales
- Service
Using support activities helps make primary activities more effective. Increasing any of the four support activities helps at least one primary activity to work more efficiently.
- Infrastructure
- Technological development
- Human resources management
- Procurement
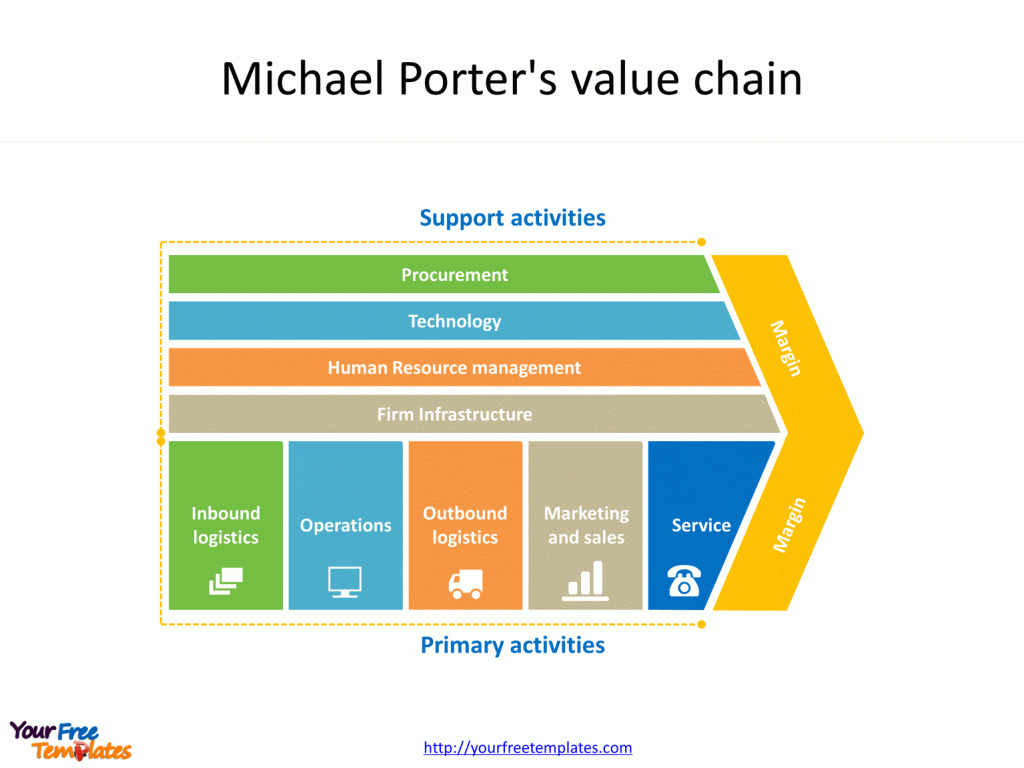
Slide 2, Arrow Process of Value Chain
The Arrow Process of value chain illustrates how materials flow from the supplier to the customer, passing through various stages of transformation. These stages represent the primary and secondary activities of the value chain.
Primary Activities
Primary activities are essential for adding value and creating a competitive advantage. They include:
-
Inbound logistics: Handling, storing, and distributing inputs of the product.
-
Operations: Transforming inputs into the final product.
-
Outbound logistics: Collecting, storing, and distributing the product to the customer.
-
Marketing and Sales: Activities that enhance product visibility and target appropriate customers.
-
Service: Activities that maintain the product and enhance the consumer experience.
Support Activities
Support activities assist primary activities by increasing their efficiency. When you boost the efficiency of any of the support activities, it benefits at least one of the primary activities.
-
Procurement: The process of acquiring raw materials.
-
Technological Development: Used during the research and development stage. It includes designing and developing manufacturing techniques and automating processes.
-
Human Resource Management: Involves hiring and retaining employees who will contribute to the company’s business strategy and product development.
-
Infrastructure: Includes company systems and the composition of its management team.
Performing a Value-Chain Analysis
Conducting a value chain analysis involves examining each primary and secondary activity to determine their efficiency and effectiveness. The steps to perform a value chain analysis include:
-
Identify sub-activities: Each primary and secondary activity should be divided into smaller sub-activities. Analyze each function to assess its contribution to the overall value.
-
Find connections: It’s crucial to identify how these sub-activities are linked. Often, inefficiencies in one activity are related to issues in another.
-
Identify improvement areas: Look for trends and patterns in sub-activities and their connections to pinpoint potential areas for improvement.
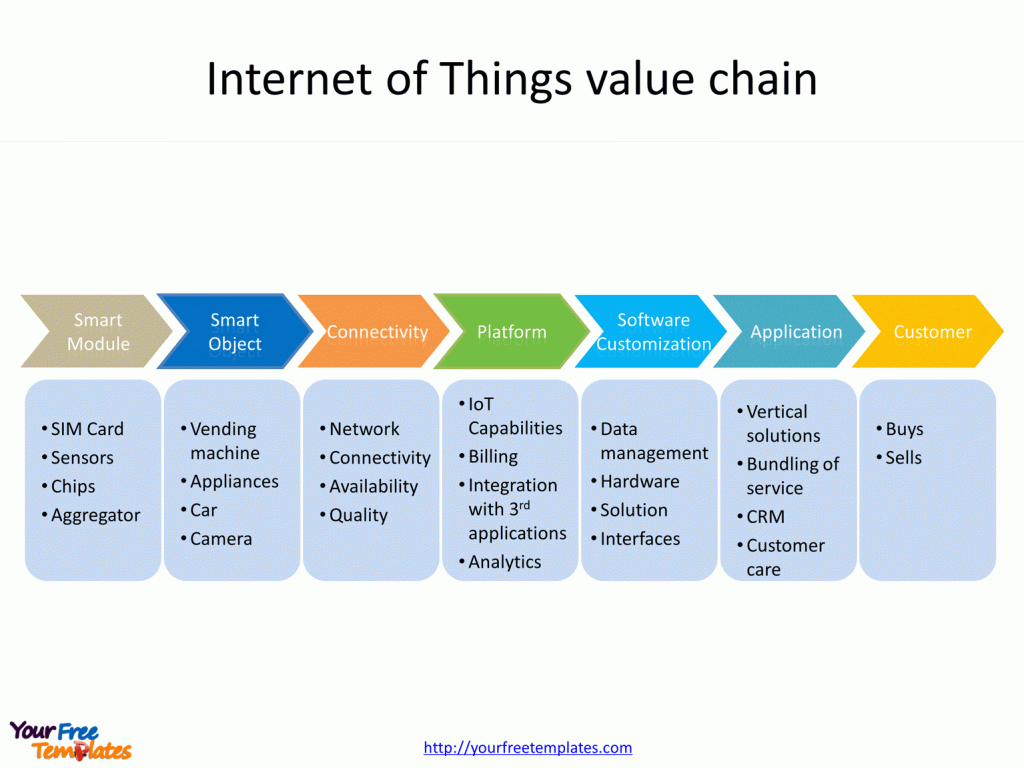
Slide 3, Internet of Things Value-Chain
The Internet of Things (IoT) is reshaping the traditional value chain by enabling real-time tracking and analysis of operations. This technology allows businesses to gain insights into their operations and customer behaviors, leading to improved efficiency and customer satisfaction. As it is applied in Internet of Things (IoT).
Benefits of Value Chain Analysis
A value chain analysis can provide several benefits, including:
-
Supporting business decisions: The analysis can provide valuable insights to inform various business decisions.
-
Identifying inefficiencies: It can help diagnose points of inefficiency for corrective action.
-
Understanding linkages: The value chain analysis can reveal dependencies and linkages between different activities.
-
Optimizing activities: It can help businesses maximize output and lower costs.
-
Establishing a competitive advantage: By highlighting areas where the business is particularly efficient, the analysis can help establish a cost advantage over competitors.
The Value Chain in Practice: Case Studies
Case Study 1: Starbucks Corporation
Starbucks offers an excellent example of a company that successfully implements the value chain concept. It is known for sourcing quality coffee beans, transforming them into a variety of beverages, and delivering a unique customer experience through its stores all around the globe.
Case Study 2: Amazon
From sourcing products from suppliers to delivering them to customers’ doorsteps, Amazon has a robust value chain. Amazon’s strong focus on technology (like cloud computing and automated warehouses) makes its operations efficient, while its customer-centric approach ensures high customer satisfaction.
Future Trends in Value Chains
Several emerging trends are set to further transform value chains. These include digital transformation, data security, privacy, customization, and personalization. Companies will need to adapt to these changes to maintain and enhance their value chains.
Conclusion
Understanding the value chain and how to analyze it can provide companies with critical insights into their operations. By identifying where value is added and where improvements can be made, companies can increase efficiency, lower costs, and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
For detailed info on it, please refer to Wikipedia.
Size:92K
Type: PPTX
[sociallocker]Aspect Ratio: Standard 4:3
Click the blue button to download it.
Download the 4:3 Template
Aspect Ratio: Widescreen 16:9
Click the green button to download it.
Download the 16:9 Template[/sociallocker]