Climate change stands as one of the most pressing challenges facing our planet today. It has an impact on every aspect of our lives, from the air we breathe to the food we eat. As global temperatures continue to rise, scientists and policymakers are working tirelessly to understand the causes of climate change and its far-reaching effects on our environment, economy, and society.
At the end of this post, you can download our Climate Change PowerPoint template to fit your purpose. As the same diagram PowerPoint template series, you can also find our Carbon Neutral Meaning, Renewable Energy Sources, Generative AI, Circular Economy, Blue Sea Strategy, 2025 Calendar with Holidays, The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People, Six Thinking Hats, Pareto Chart, Occam’s Razor, Data Mining, marketing segment, Porter’s five forces, SWOT Analysis, GE Matrix, BCG Matrix, Artificial Intelligence, National Diamond and BlockChain PowerPoint templates.
This comprehensive guide aims to explore the complex issue of climate change from various angles. It will delve into the scientific principles behind climate change, examine its observed impacts, and discuss future projections and risks. Additionally, the guide will address strategies to mitigate climate change effects and adapt to the changing environment. By providing a thorough overview, this guide seeks to equip readers with the knowledge needed to grasp the urgency of addressing climate change and the progress made in combating this global challenge.
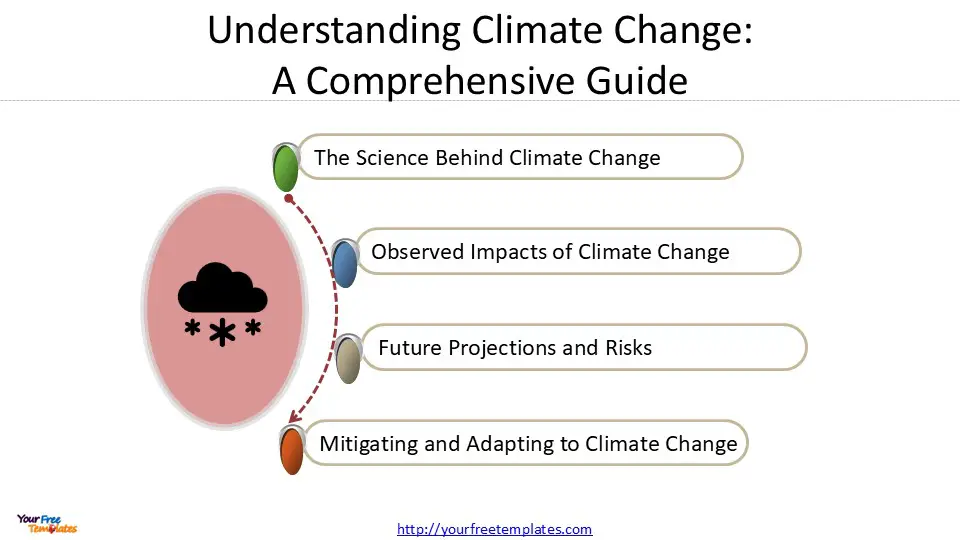
The Science Behind Climate Change
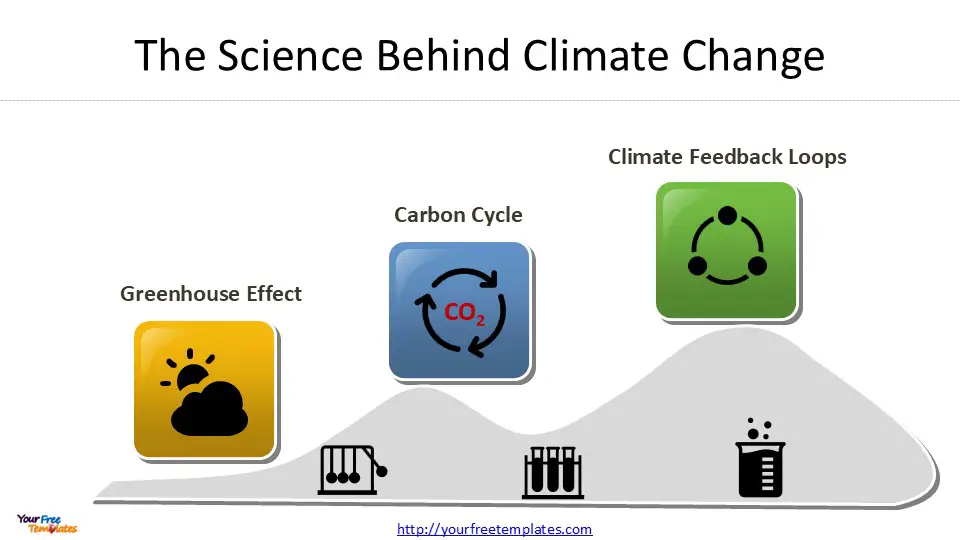
The science behind climate change is rooted in the understanding of the greenhouse effect, a natural phenomenon that keeps Earth’s surface warm. Greenhouse gasses, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, and water vapor, trap heat in the atmosphere, maintaining a temperature suitable for life. However, human activities have significantly increased the concentration of these gasses, amplifying the natural greenhouse effect and leading to global warming.
Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect occurs when gasses in the atmosphere absorb and re-emit infrared radiation from the Earth’s surface. Sunlight reaches Earth and warms the land, ocean, and atmosphere. Some of this energy is reflected back to space, but much of it is absorbed and re-radiated as heat. Greenhouse gasses then trap this heat, preventing it from escaping into space. Carbon dioxide, in particular, absorbs energy at wavelengths between 2,000 and 15,000 nanometers, overlapping with infrared energy 1.
Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate. Carbon moves between various reservoirs, including the atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms. Natural processes, such as photosynthesis and respiration, maintain a balance in the carbon cycle. However, human activities have disrupted this balance by releasing vast amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere through the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation.
Since the Industrial Revolution, atmospheric CO2 concentrations have risen from about 280 parts per million to over 420 parts per million in 2023, a 50% increase from preindustrial levels 2. This rapid increase in CO2 has led to enhanced warming of the planet.
Climate Feedback Loops
Climate feedback loops are processes that can either amplify or diminish the effects of climate change. Positive feedback loops accelerate warming, while negative feedback loops help stabilize the climate system. One example of a positive feedback loop is the water vapor feedback. As the atmosphere warms, it can hold more water vapor, which is itself a potent greenhouse gas. This additional water vapor traps more heat, leading to further warming 3.
Another significant feedback loop involves the melting of Arctic sea ice. As sea ice melts due to warming temperatures, it exposes the darker ocean surface, which absorbs more solar radiation than reflective ice. This increased absorption of heat leads to further warming and more ice melt, creating a self-reinforcing cycle.
Understanding these complex interactions and feedback mechanisms is crucial for predicting future climate changes and developing effective strategies to mitigate and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
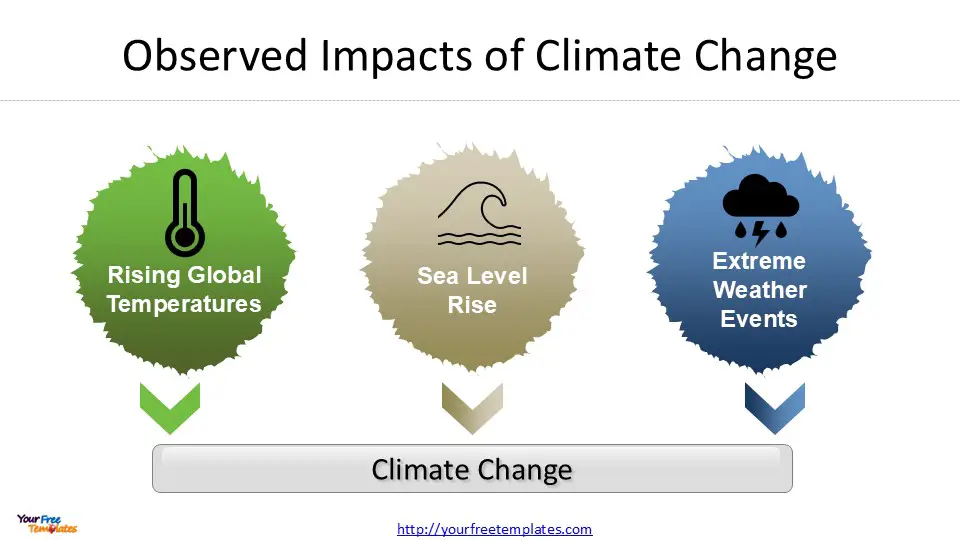
Observed Impacts of Climate Change
The effects of climate change are becoming increasingly evident across the globe, with significant impacts observed in various aspects of our environment and society. These impacts are manifesting in rising global temperatures, sea level rise, and the occurrence of extreme weather events.
Rising Global Temperatures
One of the most noticeable impacts of climate change is the increase in global temperatures. Over the past century, the Earth’s average surface temperature has risen by approximately 1.8°F (1.0°C) since 1880 1. This warming trend has accelerated in recent decades, with nine of the top 10 warmest years on record occurring since 1998 2. The rate of warming since 1982 is more than three times as fast as the long-term average, reaching 0.36°F (0.20°C) per decade 3.
The consequences of rising temperatures are far-reaching. Heat waves have become more frequent and intense, particularly in urban areas. Since the 1960s, the frequency of heat waves in major U.S. cities has tripled, with an average of six per year compared to two per year in the past 4. These extreme heat events have significant impacts on human health, agriculture, and infrastructure.
Sea Level Rise
Another critical impact of climate change is the rise in global sea levels. Since 1880, the global mean sea level has increased by about 8-9 inches (21-24 centimeters) 5. This rise is primarily due to the melting of glaciers and ice sheets, as well as the thermal expansion of seawater as it warms. The rate of sea level rise has accelerated in recent years, with the global mean sea level in 2023 reaching 101.4 millimeters (3.99 inches) above 1993 levels, the highest annual average in the satellite record 6.
The impacts of sea level rise are particularly pronounced in coastal areas, where it contributes to increased flooding, shoreline erosion, and saltwater intrusion into freshwater aquifers. In the United States, almost 30 percent of the population lives in coastal areas, making them vulnerable to these effects 7.
Extreme Weather Events
Climate change has an impact on the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. Hurricanes are growing more powerful as global temperatures rise, drawing their energy from warmer ocean waters 8. Scientists warn that storms are not only becoming stronger but are also intensifying faster. This trend has led to more destructive and costly natural disasters, affecting communities worldwide.
Droughts have also become more severe and long-lasting in many regions due to climate change. As global temperatures rise, moisture evaporates more quickly from water bodies and soil, exacerbating dry conditions 9. This has significant implications for agriculture, water resources, and ecosystems.
These observed impacts of climate change highlight the urgent need for action to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the changing climate. As the effects become more pronounced, addressing climate change remains one of the most pressing challenges facing our planet today.
Future Projections and Risks
As the effects of climate change continue to unfold, scientists are working diligently to project future scenarios and assess potential risks. These projections are crucial for understanding the long-term impacts of climate change and developing effective strategies to mitigate and adapt to these changes.
Temperature Scenarios
Climate models predict that Earth’s global average temperature will rise significantly during the 21st century if greenhouse gas emissions continue at current levels. Without swift action to reduce emissions, models project that limiting global average temperature increase to 1.5-2.0°C (2.7-3.6°F) may no longer be possible 1. Under present emission scenarios, the world is heading for a 3–4°C warming by the end of the century 2.
Even with the implementation of pledges made at COP 26 in Glasgow, the temperature rise is expected to be around 2.4°C 3. This level of warming would have severe consequences for ecosystems, human societies, and economies worldwide.
Tipping Points
One of the most concerning aspects of future climate change projections is the potential crossing of critical thresholds known as tipping points. These are points at which small changes can trigger large-scale, often irreversible shifts in Earth’s systems.
Several tipping points are already showing signs of activation. For instance, the melting of Arctic sea ice is accelerating, with some models suggesting that the Arctic Ocean could be ice-free during summer within the next few decades 4. The Greenland ice sheet is also melting at an unprecedented rate, potentially leading to significant sea-level rise 5.
Another crucial tipping point is the potential collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), a system of ocean currents that plays a vital role in regulating global climate. The slowing or stopping of the AMOC could have far-reaching consequences for weather patterns and marine ecosystems 6.
Impacts on Ecosystems and Biodiversity
Climate change is expected to have profound effects on ecosystems and biodiversity worldwide. As temperatures rise, many species are being forced to adapt or migrate to new habitats. However, the rapid pace of climate change is making it difficult for many species to keep up.
Coral reefs, which are home to a quarter of all marine species, are particularly vulnerable to climate change. If global temperatures rise by 2°C, it is projected that 99% of coral reefs will experience severe bleaching events 7. This could lead to the collapse of entire marine ecosystems and have devastating impacts on the millions of people who depend on them for food and livelihoods.
Terrestrial ecosystems are also at risk. The Amazon rainforest, often referred to as the “lungs of the Earth,” is facing increased threats from climate change-induced droughts and wildfires. If these trends continue, large portions of the Amazon could transition from rainforest to savannah, releasing massive amounts of stored carbon and further accelerating global warming 8.
As we look to the future, it is clear that the impacts of climate change will be far-reaching and potentially catastrophic if left unchecked. However, these projections also underscore the urgent need for action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and build resilience in our natural and human systems.
Mitigating and Adapting to Climate Change
As the effects of climate change become increasingly evident, efforts to mitigate its impacts and adapt to the changing environment have gained urgency. Addressing this global challenge requires a multi-faceted approach that involves reducing emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and implementing strategies to build resilience in communities worldwide.
Reducing Emissions
One of the most critical steps in mitigating climate change is reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This involves a concerted effort across various sectors, including transportation, industry, and energy production. In the United States, the average person produces 21 tons of carbon dioxide annually, which is about four times the global average 1. To address this, individuals can make significant contributions by adopting more sustainable practices in their daily lives.
Simple measures, such as adjusting thermostats, can have a substantial impact. Lowering the thermostat by 3 degrees Fahrenheit in winter and raising it by the same amount in summer can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by approximately 1,050 pounds per year 2. Additionally, using programmable thermostats can further decrease emissions by giving heating and cooling systems a break during periods of low activity.
Renewable Energy
The transition to renewable energy sources is crucial in the fight against climate change. Solar and wind energy have experienced remarkable growth and cost improvements over the past decade. In fact, the cost of generating electricity from wind and solar has declined by 58 percent and 78 percent, respectively, since 2009 3. This trend is expected to continue, making renewable energy increasingly competitive with fossil fuels.
Many countries are making significant progress in adopting renewable energy. For instance, Iceland and Costa Rica now generate nearly all of their electricity from renewable sources 4. In the United States, wind energy accounted for just above 9 percent of electricity generation in recent years, with projections indicating substantial growth in the coming decades 5.
Climate Adaptation Strategies
While mitigation efforts are essential, adapting to the impacts of climate change that are already occurring is equally important. Climate adaptation strategies involve adjusting to actual or expected climate effects to reduce risks and capitalize on potential opportunities.
One crucial aspect of adaptation is improving the resilience of infrastructure. This includes implementing measures such as building flood defenses, planning for heat waves, and installing better-draining pavements to deal with floods and stormwater 6. These strategies help communities withstand the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events associated with climate change.
Another important adaptation strategy involves protecting and enhancing natural ecosystems. Planting trees, conserving forests, and restoring wetlands not only help absorb carbon dioxide but also provide numerous benefits for biodiversity and human well-being. These nature-based solutions can play a significant role in building resilience to climate impacts while simultaneously contributing to mitigation efforts.
As we continue to face the challenges posed by climate change, it is clear that a combination of mitigation and adaptation strategies will be necessary. By reducing emissions, embracing renewable energy, and implementing adaptive measures, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient future.
Conclusion
The comprehensive exploration of climate change underscores its far-reaching effects on our planet and society. From rising temperatures and sea levels to extreme weather events, the impacts are already evident and projected to intensify. This guide has shed light on the science behind climate change, its observed effects, and the risks we face in the future. It’s clear that addressing this global challenge requires immediate and sustained action.
To tackle climate change effectively, a multi-pronged approach is necessary. This involves reducing emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and implementing strategies to adapt to the changing environment. By understanding the complexities of climate change and taking decisive steps to mitigate its effects, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient future. The time to act is now, as our collective efforts today will shape the world we leave for future generations.
FAQs
What are some essential questions to ask about climate change?
Some important questions include: Why are there record-breaking cold temperatures and snowfalls in my town despite global warming? Is there a consensus among scientists that human activities are driving current climate changes? Do natural climate variations also play a role in the changes we observe today?
What are seven questions about the climate crisis that might seem too basic to ask?
Here are seven straightforward questions about the climate crisis:
- What exactly does “climate change” mean?
- What are the causes of climate change?
- Could this just be a part of natural climatic cycles?
- Why is climate change considered a problem?
- Is there a unanimous agreement among scientists regarding climate change?
- What are the current impacts of climate change on our planet?
What should everyone understand about climate change?
Climate change refers to long-term alterations in typical weather patterns. This phenomenon manifests through various signs, such as shifts in precipitation patterns, more frequent droughts, increased flooding, and intense heatwaves.
What are six critical facts everyone should know about climate change?
Here are six alarming facts concerning climate change:
- Climate change might become irreversible by 2030.
- Levels of greenhouse gasses are higher than ever before.
- Over a million species are at risk of extinction due to climate change.
- Climate change is contributing to a global refugee crisis.
- The health of our oceans is in severe decline.
- Humanity is consuming resources faster than the Earth can replenish them.
Size:350K
Type: PPTX
Climate Change Template
Click the link to download it.
Aspect Ratio: Standard 4:3
Click the blue button to download it.
Download the 4:3 Template
Aspect Ratio: Widescreen 16:9
Click the green button to download it.
Download the 16:9 Template
References
[1] – https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/what-is-climate-change
[2] – https://science.nasa.gov/climate-change/what-is-climate-change/
[3] – https://climateknowledgeportal.worldbank.org/overview
[4] – https://www.un.org/en/global-issues/climate-change
[5] – https://lpsonline.sas.upenn.edu/features/why-its-important-learn-about-climate-change
[6] – https://ncas.ac.uk/learn/why-is-climate-important/
[7] – https://www.iberdrola.com/social-commitment/climate-change-education
[8] – https://www.mooc.org/blog/why-is-it-important-to-study-climate-change
[9] – https://www.epa.gov/climatechange-science/basics-climate-change