As a business owner or manager, staying ahead of the competition is crucial to the success of your business. One of the most effective ways to do this is by mastering the art of competitive strategy. And, when it comes to competitive strategy, Michael Porter is a name that stands out. The professor is credited for creating great works, Including Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Strategy, National Diamond, and Value Chain. In this blog, we present 12 slides which are centering Diamond Theory but also covering the other three models developed by Michael Porter.
Introduction to Michael Porter and the Diamond Theory
Michael Porter is a renowned professor at Harvard Business School and a leading authority on competitive strategy. He is best known for his work on the Diamond Theory, which is a framework for analyzing the competitive environment of an industry.
The Diamond Theory suggests that the competitiveness of an industry is determined by four key components: factor conditions, related and supporting industries, firm strategy, structure and rivalry, and demand conditions. By understanding these components, businesses can develop effective strategies to gain a competitive advantage.
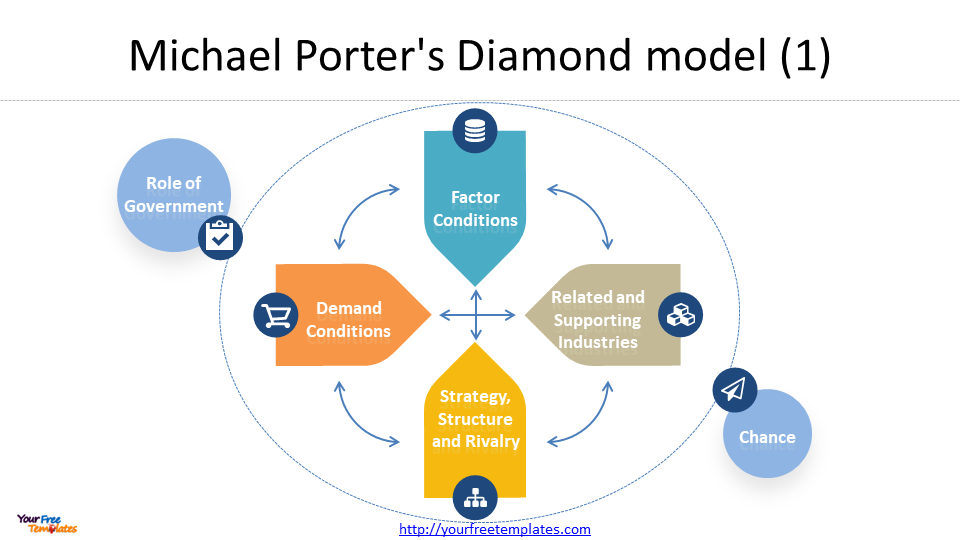
Overview of the Diamond Theory framework
The Diamond Theory is based on the idea that the competitiveness of an industry is determined by a variety of factors that interact with each other. These factors are represented by a diamond-shaped framework, with each point representing one of the four key components of the theory.
- In the diamond model, the first aspect pertains to factor conditions, which signifies the resources and infrastructure that are accessible in a specific area, such as natural resources, labor, capital, and technology.
- The second element of the diamond model is related and supporting industries, which denotes the presence of other organizations that help the industry, such as suppliers, distributors, and other related businesses.
- The third point of the diamond model stands for firm strategy, structure, and rivalry, which refers to the way companies compete with each other, including pricing, marketing, and product development.
- The fourth and last aspect of the diamond model pertains to demand conditions, which denotes the level of demand for the product or service, including consumer preferences, income levels, and population demographics.
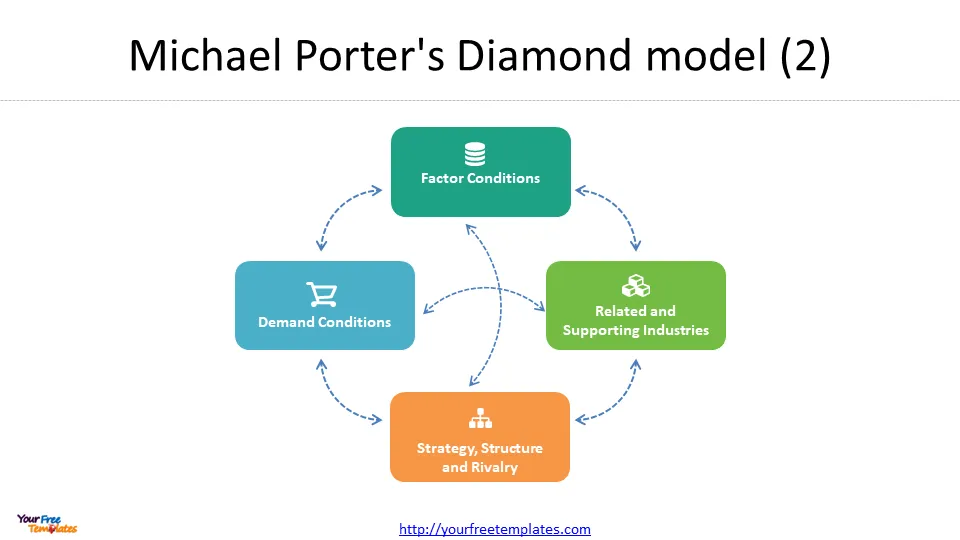
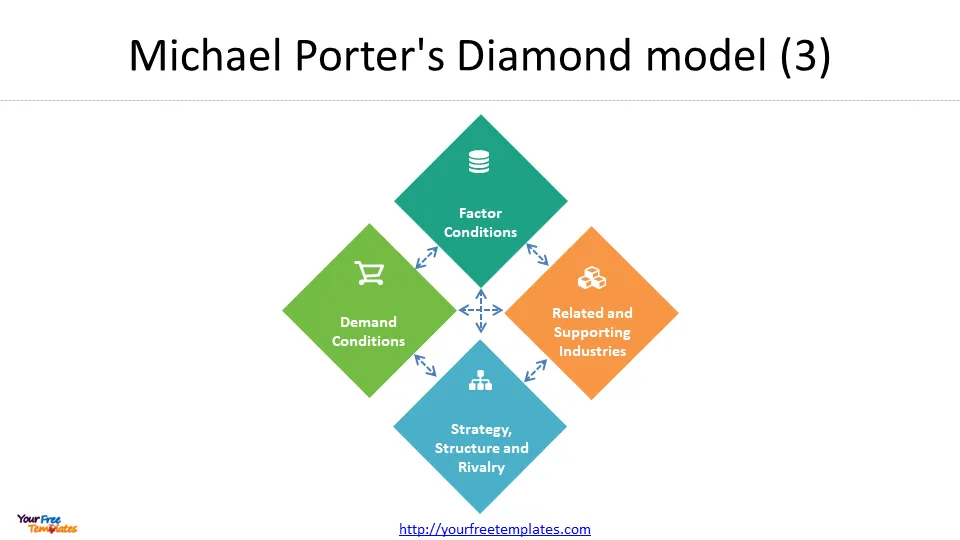
Understanding the four components of the Diamond Theory
Each of the four components of the Diamond Theory plays a critical role in determining the competitiveness of an industry. Here is a more detailed look at each component:
1. Factor conditions
Factor conditions refer to the resources and infrastructure that are available in a particular location. This includes things like natural resources, labour, capital, and technology. These resources can be either basic or advanced.
Basic resources include things like land, water, and minerals. Advanced resources include things like skilled labour, scientific research, and a strong transportation infrastructure.
The quality and availability of these resources can have a significant impact on the competitiveness of an industry. For example, a location with a strong transportation infrastructure can make it easier and cheaper for businesses to transport goods and materials, which can lead to lower costs and higher profits.
2. Related and supporting industries
Related and supporting industries refer to the presence of other businesses that support the industry. This includes things like suppliers, distributors, and other related industries.
Having a strong network of related and supporting industries can help businesses in an industry to be more competitive. For example, a company that produces car parts might rely on a network of suppliers to provide the raw materials and components needed to produce those parts. If those suppliers are unreliable or expensive, it can hurt the competitiveness of the car parts industry as a whole.
3. Firm strategy, structure and rivalry
Firm strategy, structure and rivalry refer to the way that companies compete with each other. This includes things like pricing, marketing, and product development.
The way that businesses compete with each other can have a significant impact on the competitiveness of an industry. For example, if a company in an industry can develop a product that is significantly better than the products of its competitors, it may be able to capture a larger share of the market.
4. Demand conditions
Demand conditions refer to the level of demand for the product or service. This includes factors like consumer preferences, income levels, and population demographics.
The level of demand for a product or service can have a significant impact on the competitiveness of an industry. For example, if there is a high demand for a particular product, it may be easier for businesses in that industry to be profitable.
Comparing Porter’s Five Forces, the Value Chain analysis and Competitive Strategy to the Diamond Theory.
The Diamond Theory is often compared to the other frameworks developed by Michael Porter: the Five Forces model, the Value Chain analysis.
The Five Forces model is a framework for analyzing the competitive environment of an industry. It suggests that the competitiveness of an industry is influenced by five key forces: the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers, the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
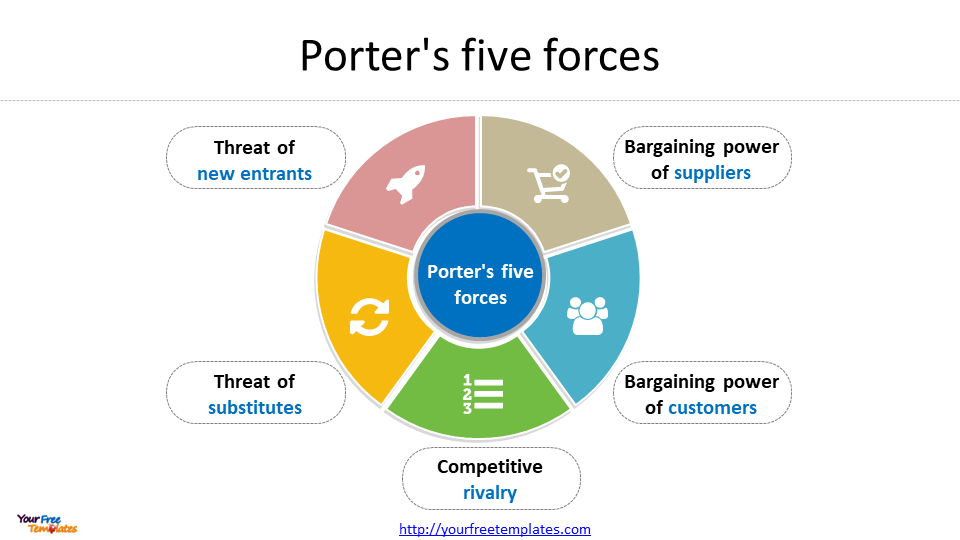
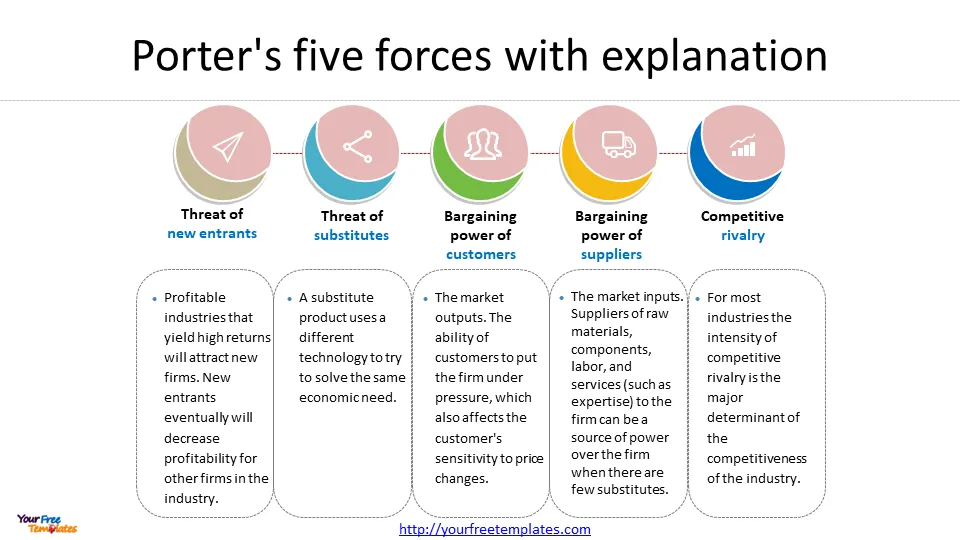
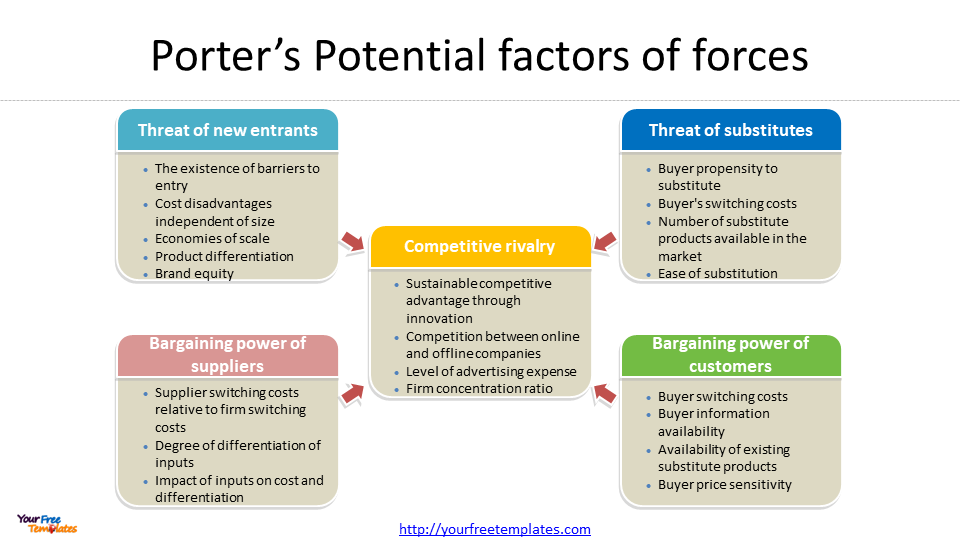 The Value Chain analysis is a framework for analyzing a company’s internal operations. It suggests that a company can create value by optimizing its internal processes and activities.
The Value Chain analysis is a framework for analyzing a company’s internal operations. It suggests that a company can create value by optimizing its internal processes and activities.
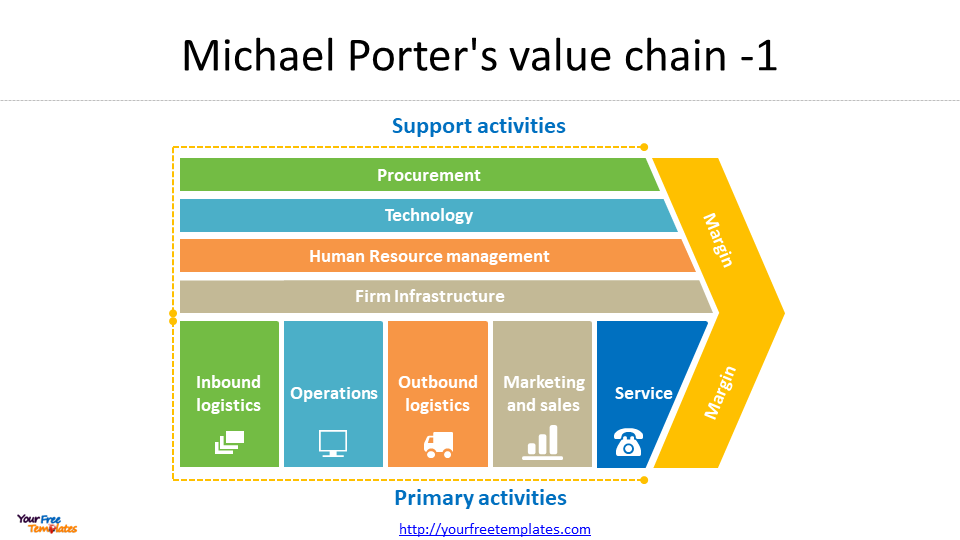
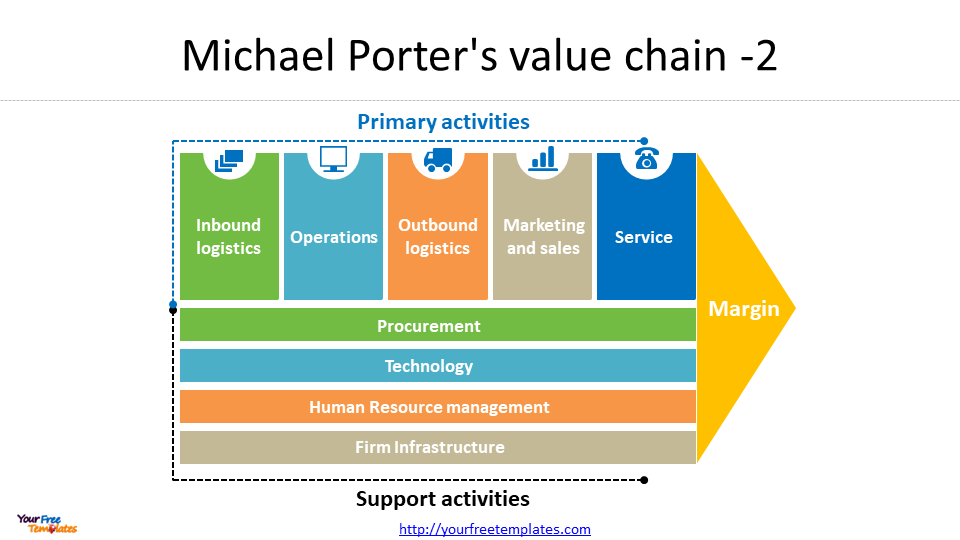 While the Diamond Theory, Five Forces model, and Value Chain analysis all share some similarities, they each focus on different aspects of competitiveness. The Diamond Theory is focused on the external factors that influence an industry’s competitiveness, while the Five Forces model and Value Chain analysis are focused on the internal and external factors that influence a company’s competitiveness.
While the Diamond Theory, Five Forces model, and Value Chain analysis all share some similarities, they each focus on different aspects of competitiveness. The Diamond Theory is focused on the external factors that influence an industry’s competitiveness, while the Five Forces model and Value Chain analysis are focused on the internal and external factors that influence a company’s competitiveness.
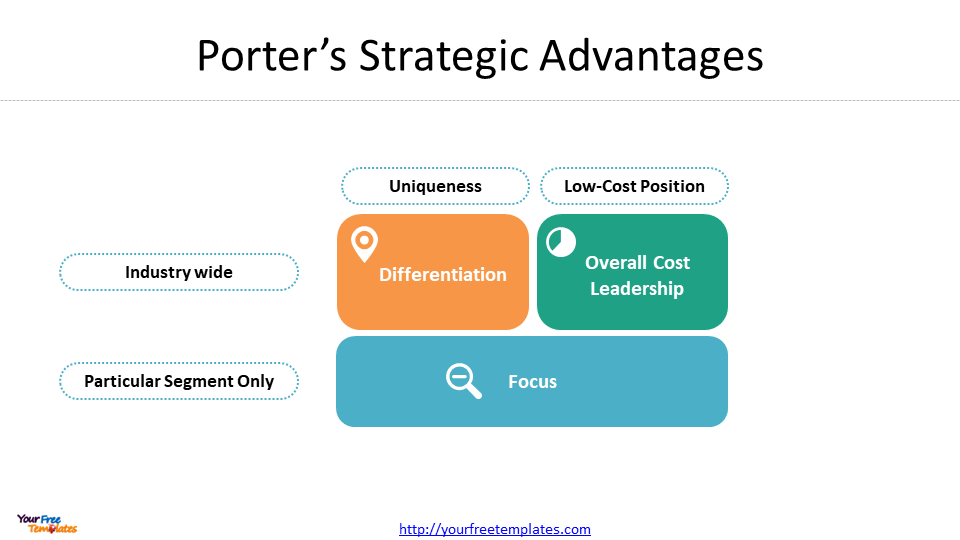
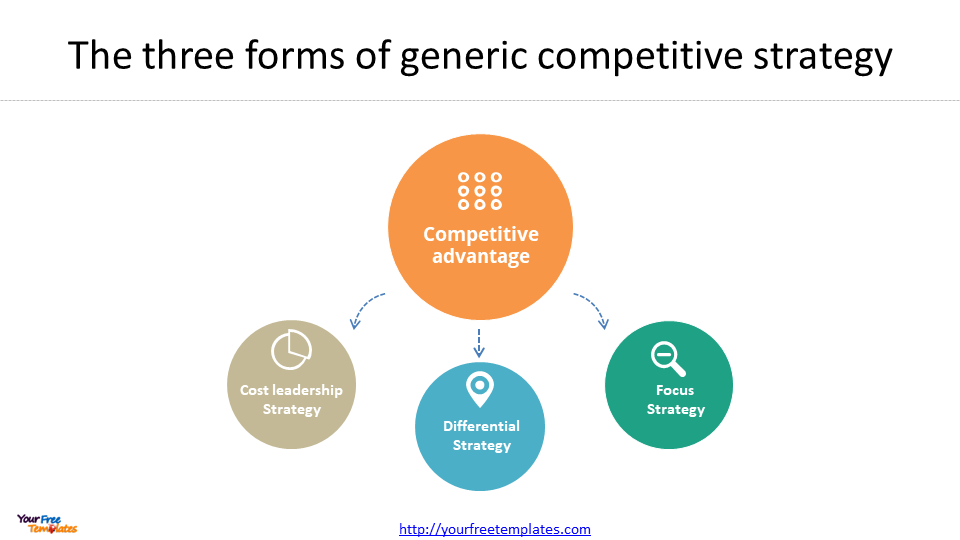
While Porter’s Competitive Strategy framework is based on the idea that businesses need to choose a clear and distinctive positioning in the market to be successful. The framework identifies three generic strategies that businesses can use to achieve this positioning:
- Cost leadership: Offering products or services at a lower cost than competitors
- Differentiation: Offering products or services that are perceived as unique or superior to competitors
- Focus: Narrowing the target market to a specific niche and tailoring products or services to meet their needs
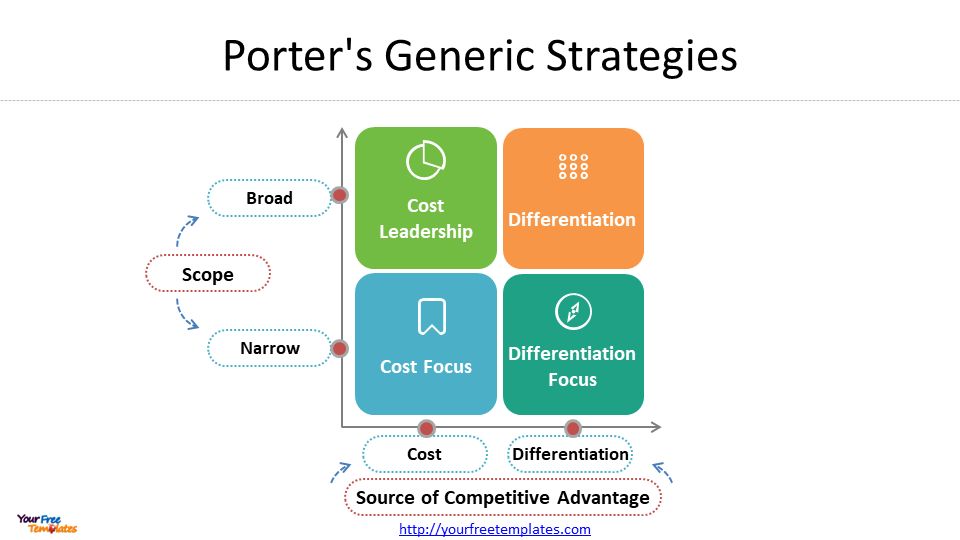 By choosing one of these strategies and executing it effectively, businesses can create a sustainable competitive advantage and outperform their competitors.
By choosing one of these strategies and executing it effectively, businesses can create a sustainable competitive advantage and outperform their competitors.
 Examples of the Diamond Theory in action – case studies of successful companies
Examples of the Diamond Theory in action – case studies of successful companies
There are many examples of companies that have successfully applied the Diamond Theory to gain a competitive advantage. Here are just a few:
1. Apple
Apple is a company that has been able to gain a significant competitive advantage by leveraging the resources and infrastructure available in the Silicon Valley region of California. Silicon Valley has a strong network of related and supporting industries, including suppliers of components and materials, software developers, and other technology companies. Apple has also been able to develop a strong brand and product strategy that sets it apart from its competitors.
2. Toyota
Toyota is a company that has been able to gain a significant competitive advantage by optimizing its internal operations using the Value Chain analysis. The company has focused on creating value by improving its manufacturing processes, reducing waste, and optimizing its supply chain. This has allowed Toyota to produce high-quality cars at a lower cost than its competitors.
3. Amazon
Amazon is a company that has been able to gain a significant competitive advantage by leveraging its strong customer demand and using innovative technology to optimize its operations. The company has invested heavily in its logistics and distribution network, which has allowed it to offer fast and reliable delivery to its customers. Amazon has also been able to use data analytics and machine learning to personalize the shopping experience for each customer.
Limitations of the Diamond Theory
While the Diamond Theory is a powerful framework for analyzing the competitive environment of an industry, it has some limitations. One of the main limitations is that it is focused primarily on the external factors that influence an industry’s competitiveness. It does not take into account the internal factors that can also have a significant impact on a company’s competitiveness.
Another limitation of the Diamond Theory is that it is a relatively static framework. It does not take into account the dynamic nature of industries and the way that they can change over time.
Applying the Diamond Theory to your own business – tips and strategies
If you want to apply the Diamond Theory to your own business, there are a few tips and strategies that you can use:
1. Conduct a thorough analysis of your industry
The first step in applying the Diamond Theory to your own business is to conduct a thorough analysis of your industry. This will involve looking at the four key components of the Diamond Theory and determining how they apply to your industry.
2. Identify your company’s strengths and weaknesses
Once you have analyzed your industry, the next step is to identify your company’s strengths and weaknesses. This will involve looking at your company’s internal operations and determining where you are doing well and where you need to improve. Here SWOT analysis tool or GE Matrix can be helphul.
3. Develop a strategy to gain a competitive advantage
Once you have identified your company’s strengths and weaknesses, the next step is to develop a strategy to gain a competitive advantage. This will involve leveraging your company’s strengths and addressing its weaknesses. You can also try TOWS stragegy to identify the best strategy combination.
4. Monitor and adjust your strategy over time
Finally, it is important to monitor and adjust your strategy over time. Industries are dynamic and can change quickly, so it is important to stay up-to-date on the latest trends and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Resources for further learning about the Diamond Theory and Competitive Strategy
If you want to learn more about the Diamond Theory and Competitive Strategy, there are a number of resources available. Here are a few:
- Michael Porter’s book “Competitive Strategy“
- Michael Porter’s book “The Competitive Advantage of Nations“
- Michael Porter’s other book “Porter’s Five Forces” and “Value Chain“
- Harvard Business Review articles on Competitive Strategy
- Online courses on Competitive Strategy
Conclusion
Mastering the art of competitive strategy is crucial to the success of any business. By using frameworks like the Diamond Theory, businesses can gain a better understanding of the competitive environment of their industry and develop effective strategies to gain a competitive advantage. While the Diamond Theory has some limitations, it is a powerful tool that can help businesses stay ahead of the competition.
For other interesting maps, pls visit our ofomaps.com
Size:125K
Type: PPTX
Aspect Ratio: Standard 4:3
Click the blue button to download Michael Porter 4 Models.
Download the 4:3 Template
Aspect Ratio: Widescreen 16:9
Click the green button to download Michael Porter 4 Models..
Download the 16:9 Template