The SPACE Matrix is a powerful tool in strategic management that helps organizations evaluate their strategic position and determine appropriate actions. This analytical framework considers internal and external factors to provide insights into a company’s competitive advantage and strategic positioning. By assessing factors such as financial strength, industry stability, and competitive pressures, the SPACE Matrix enables businesses to make informed decisions about their strategic direction.
At the end of this post, you can download our SPACE Matrix PowerPoint template to fit your purpose. As the same diagram PowerPoint template series, you can also find our Bowman’s Strategy Clock, Value Chain Analysis, Climate Change, Carbon Neutral Meaning, Renewable Energy Sources, Generative AI, Circular Economy, Blue Sea Strategy, 2025 Calendar with Holidays, The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People, Six Thinking Hats, Pareto Chart, Occam’s Razor, Data Mining, marketing segment, Porter’s five forces, SWOT Analysis, GE Matrix, BCG Matrix, Artificial Intelligence, National Diamond and BlockChain PowerPoint templates.
This article will guide readers through the process of using the SPACE Matrix for strategic analysis. It will cover the fundamentals of the SPACE Matrix, explain how to conduct a SPACE analysis, and discuss the strategic implications of the results. Additionally, the article will explore how to implement insights gained from the SPACE Matrix to improve a company’s strategic position and cash flow. Readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of this valuable tool for strategic decision-making and its role in enhancing competitive advantage.
Understanding the SPACE Matrix
The SPACE Matrix, which stands for Strategic Position and Action Evaluation, is a powerful tool in strategic management that helps organizations assess their competitive position and determine appropriate strategic actions. This analytical framework considers both internal and external factors to provide insights into a company’s strategic positioning and competitive advantage.
Components of the SPACE Matrix
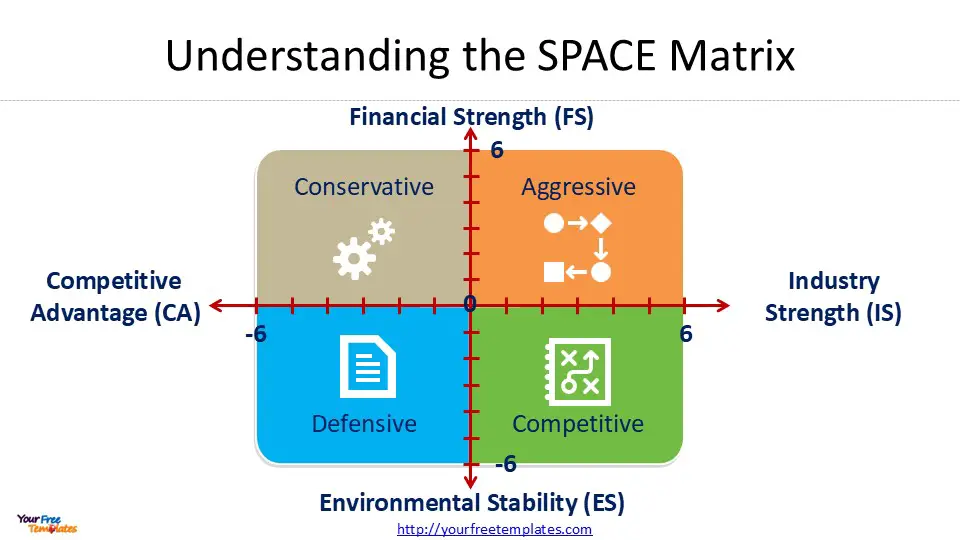
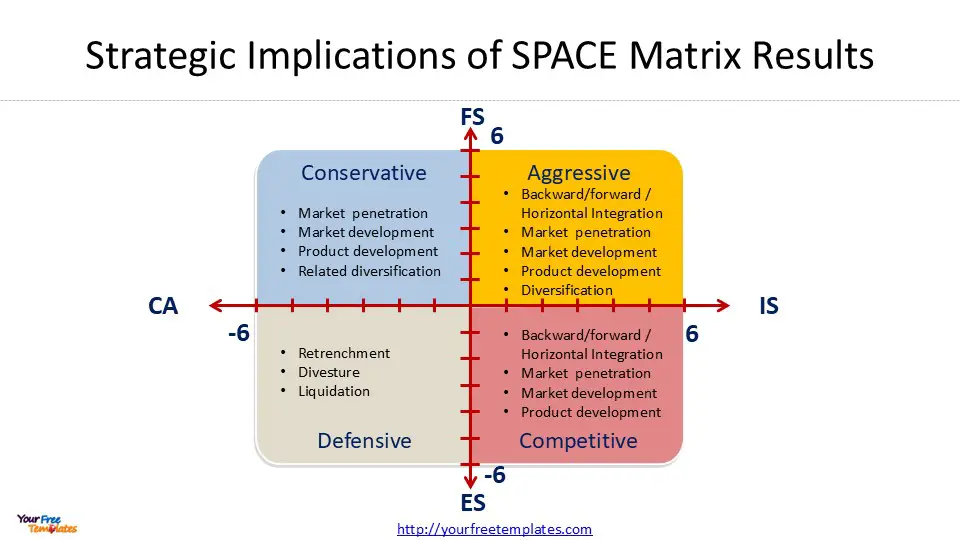
The SPACE Matrix is divided into four quadrants, each representing a different strategic posture: Aggressive, Conservative, Defensive, and Competitive. These quadrants are formed by two axes that represent internal and external strategic dimensions.
The internal strategic dimensions include:
- Financial Strength (FS): This dimension evaluates factors such as cash flow, inventory turnover, and return on investment.
- Competitive Advantage (CA): This considers elements like market share, product quality, and customer loyalty.
The external strategic dimensions consist of:
- Environmental Stability (ES): This assesses factors such as technological changes, price elasticity of demand, and inflation rate.
- Industry Strength (IS): This examines aspects like growth potential, profit potential, and barriers to entry.
Scoring the SPACE Matrix Dimensions
To construct a SPACE Matrix, organizations need to follow a systematic approach:
- Select relevant variables for each dimension (FS, CA, ES, and IS).
- Rate individual factors using a specific scale for each dimension:
- For ES and CA: Use a scale from -6 (worst) to -1 (best)
- For FS and IS: Use a scale from +1 (worst) to +6 (best)
- Calculate average scores for each dimension.
- Plot the scores on the appropriate axes of the matrix.
- Add the scores for IS and CA to determine the X-axis endpoint.
- Add the scores for FS and ES to determine the Y-axis endpoint.
- Draw a directional vector from the origin to the intersection point of X and Y.
Interpreting the SPACE Matrix Results
The resulting vector indicates the type of strategy an organization should pursue:
- Aggressive Strategy: This suggests that the company has high financial strength, strong competitive advantages, and operates in an attractive industry with relative environmental stability.
- Competitive Strategy: This indicates limited financial strength but medium competitive advantage in an attractive industry, operating in a relatively unstable environment.
- Conservative Strategy: This implies that the company has limited competitive advantage in a less attractive industry but enjoys financial strength and operates in a stable environment.
- Defensive Strategy: This suggests that the company lacks both competitive advantage and financial strength, operates in an unattractive industry, and faces an unstable environment.
By using the SPACE Matrix, organizations can gain valuable insights into their strategic position and make informed decisions about their future direction. This tool complements other strategic analyzes, such as the SWOT analysis or BCG matrix, providing a comprehensive view of an organization’s strategic landscape and helping to formulate effective strategies for enhancing competitive advantage and improving cash flow.
Conducting a SPACE Analysis
Conducting a SPACE (Strategic Position and Action Evaluation) analysis involves a systematic approach to evaluate a company’s strategic position and determine appropriate actions. This process requires careful consideration of both internal and external factors that influence an organization’s competitive advantage and strategic positioning.
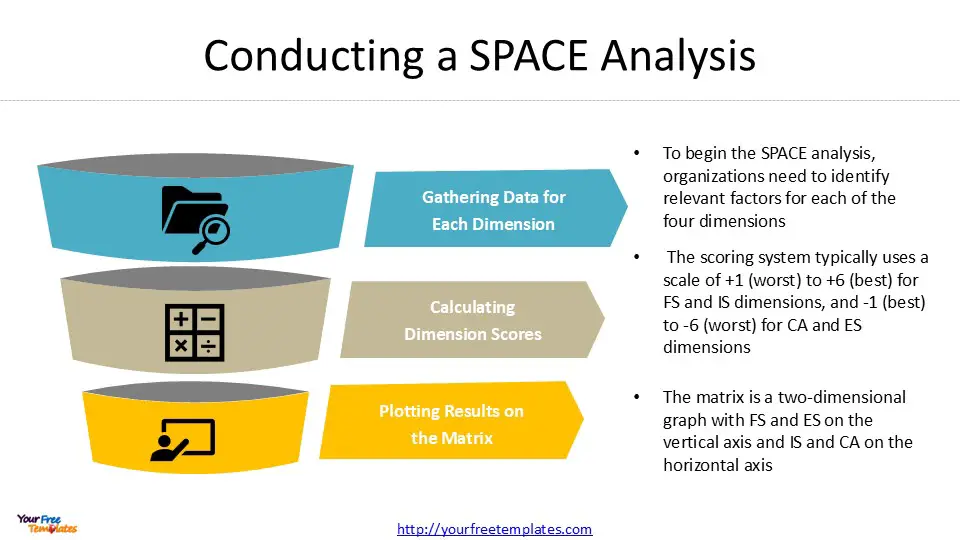
Gathering Data for Each Dimension
To begin the SPACE analysis, organizations need to identify relevant factors for each of the four dimensions: Financial Strength (FS), Competitive Advantage (CA), Industry Strength (IS), and Environmental Stability (ES). These factors should accurately reflect the company’s position and the industry landscape.
For Financial Strength, companies should consider metrics such as return on investment, cash flow, and liquidity. Competitive Advantage factors may include market share, product quality, and customer loyalty. Industry Strength can be assessed through growth potential, profit potential, and barriers to entry. Environmental Stability factors might encompass technological changes, price elasticity of demand, and inflation rates.
It’s crucial to select factors that are most relevant to the specific industry and company. For instance, in the energy services industry, factors like technological know-how and control over suppliers may be particularly important for competitive advantage.
Calculating Dimension Scores
Once the relevant factors are identified, the next step is to assign numerical values to each factor. The scoring system typically uses a scale of +1 (worst) to +6 (best) for FS and IS dimensions, and -1 (best) to -6 (worst) for CA and ES dimensions.
After assigning scores to individual factors, calculate the average score for each dimension. This is done by summing the values given to the factors within a dimension and dividing by the number of factors included. For example, if five factors are chosen for Financial Strength, the sum of their scores would be divided by five to obtain the average FS score.
Plotting Results on the Matrix
With the average scores calculated, it’s time to plot the results on the SPACE matrix. The matrix is a two-dimensional graph with FS and ES on the vertical axis, and IS and CA on the horizontal axis.
To plot the points:
- On the horizontal axis, plot the average CA score on the left (negative) side and the average IS score on the right (positive) side.
- On the vertical axis, plot the average ES score below the origin (negative) and the average FS score above the origin (positive).
- Calculate the x-coordinate by adding the CA and IS scores.
- Calculate the y-coordinate by adding the ES and FS scores.
- Plot the intersection point of these coordinates on the matrix.
Finally, draw a directional vector from the origin through the intersection point. This vector reveals the type of strategy recommended for the organization, falling into one of four categories: aggressive, competitive, conservative, or defensive.
By following this structured approach, organizations can gain valuable insights into their strategic position and make informed decisions about their future direction. The SPACE matrix complements other strategic management tools, providing a comprehensive view of an organization’s strategic landscape and helping to formulate effective strategies for enhancing competitive advantage and improving cash flow.
Strategic Implications of SPACE Matrix Results
The SPACE Matrix provides valuable insights into an organization’s strategic position, enabling decision-makers to determine the most appropriate course of action. By analyzing the results of the SPACE Matrix, companies can identify their strategic priorities and develop effective strategies to enhance their competitive advantage and improve cash flow.
Aggressive Strategy
When a company’s SPACE Matrix results indicate an aggressive posture, it signifies strong financial strength and favorable industry conditions. Organizations in this position have the opportunity to fully exploit available opportunities and enhance their market share 1. These companies often invest heavily in research and development, market expansion, and innovation to capitalize on opportunities and gain a competitive advantage 2.
To implement an aggressive strategy, companies should:
- Continue to invest in innovation to sustain and build competitive advantage
- Aggressively build market share by moving above the fair value line in the customer value map
- Pursue growth through acquisitions or vertical integration
- Raise the stakes for competitors through rapid product innovations or marketing campaigns
Conservative Strategy
A conservative posture in the SPACE Matrix suggests that a company has strong financial strength and operates in a stable environment but faces limited market opportunities 3. Organizations in this position should focus on optimizing existing resources, maintaining a strong financial position, and improving operational efficiency 2.
Key actions for a conservative strategy include:
- Focusing on existing successful products and developing new ones cautiously
- Trimming costs and eliminating loss-making customers and products
- Exploring profitable diversification opportunities
- Identifying and focusing on attractive market niches
Defensive Strategy
Companies in a defensive posture typically face challenges in their external environment and lack both competitive advantage and financial strength 3. This position requires organizations to adopt strategies aimed at protecting their market share, reducing costs, and strengthening customer loyalty 2.
To implement a defensive strategy, companies should:
- Discontinue non-viable products and tightly control costs
- Monitor cash flows strictly and reduce capacity
- Postpone or limit investments
- Focus on product differentiation to maintain competitive position
Competitive Strategy
A competitive posture indicates that a company has a strong competitive advantage and operates in favorable industry conditions but may face environmental instability or limited financial strength 3. Organizations in this position should focus on increasing market share, expanding product offerings, and enhancing customer satisfaction 2.
Key actions for a competitive strategy include:
- Improving or differentiating products to maintain and enhance competitive advantage
- Widening the product line and improving marketing effectiveness
- Mobilizing and augmenting financial resources
- Continuously innovating and investing in marketing and branding
By understanding the strategic implications of their SPACE Matrix results, organizations can make informed decisions regarding resource allocation and strategic direction. This analysis helps companies identify the most appropriate strategies to enhance their competitive advantage, improve cash flow, and navigate the complexities of their market landscape effectively.
Implementing SPACE Matrix Insights
After conducting a SPACE Matrix analysis, organizations must translate the insights gained into actionable strategies. This process involves aligning business objectives, developing comprehensive action plans, and continuously monitoring and adjusting the chosen strategy.
Aligning Business Objectives
To effectively implement SPACE Matrix insights, organizations need to align their business objectives with the strategic direction indicated by the analysis. This alignment ensures that the company’s goals and resources are focused on leveraging its strengths and addressing weaknesses identified through the SPACE Matrix.
For instance, if the SPACE Matrix suggests an aggressive strategy, the company should set objectives that capitalize on its strong financial position and competitive advantage. These objectives might include expanding market share, investing in research and development, or pursuing acquisitions to enhance its position in the industry.
Conversely, if the analysis indicates a defensive posture, the organization should focus on objectives that aim to protect its market share, reduce costs, and strengthen customer loyalty. In this case, the company might prioritize objectives related to improving operational efficiency, streamlining product offerings, or enhancing customer retention programs.
Developing Action Plans
Once business objectives are aligned with the SPACE Matrix insights, the next step is to develop detailed action plans. These plans should outline specific steps, timelines, and resource allocations necessary to achieve the strategic goals identified through the analysis.
For example, if the SPACE Matrix suggests a competitive strategy, the action plan might include:
- Improving or differentiating products to maintain and enhance competitive advantage
- Widening the product line and improving marketing effectiveness
- Mobilizing and augmenting financial resources
- Continuously innovating and investing in marketing and branding
Each action item should have clear ownership, measurable targets, and defined timelines to ensure accountability and track progress effectively.
Monitoring and Adjusting Strategy
Implementing SPACE Matrix insights is not a one-time event but an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. Organizations should establish key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with their strategic objectives and regularly assess progress against these metrics.
Regular reassessment of the SPACE Matrix is crucial, as market conditions and internal factors can change over time. By conducting periodic SPACE analyzes, companies can identify shifts in their strategic position and make necessary adjustments to their strategies.
For instance, if a company initially pursued an aggressive strategy but later finds its financial strength weakening, it may need to shift towards a more conservative approach. This might involve reassessing resource allocation, reevaluating expansion plans, or focusing on cost optimization initiatives.
By implementing SPACE Matrix insights through aligned objectives, detailed action plans, and continuous monitoring, organizations can enhance their strategic positioning and improve their competitive advantage in the dynamic business landscape.
Conclusion
The SPACE Matrix stands out as a valuable tool to evaluate a company’s strategic position and guide decision-making. By examining internal and external factors, it provides a clear picture of an organization’s competitive landscape and helps identify the most suitable strategic approach. This analysis has a significant impact on strategic planning, allowing businesses to align their objectives, develop targeted action plans, and make informed choices about resource allocation.
To wrap up, the effective use of the SPACE Matrix requires a commitment to ongoing assessment and adaptation. As market conditions shift and internal factors evolve, companies must regularly revisit their analysis to ensure their strategies remain relevant and effective. By using the SPACE Matrix as part of a comprehensive strategic management process, organizations can boost their competitive edge, improve cash flow, and position themselves for long-term success in today’s fast-paced business world.
FAQs
What is the SPACE Matrix in the context of strategic positioning and action evaluation?
The Strategic Position and Action Evaluation (SPACE) Matrix is an analytical tool used in strategic management. It helps organizations assess their competitive stance by analyzing both internal and external strategic dimensions.
How is the SPACE Matrix constructed in strategic management?
To construct the SPACE Matrix, values representing an organization’s financial strength, competitive advantage, industry strength, and environmental stability are combined. These values are then averaged and plotted along the axes of the SPACE Matrix to provide a visual representation of strategic positioning.
Is the SPACE Matrix essential for strategic planning?
Yes, the SPACE Matrix is considered a crucial tool for strategic planning. It provides a clear visual layout that helps organizations understand their strategic position, aiding in informed decision-making and the development of effective strategies to meet business goals.
How do you interpret the results shown on a SPACE Matrix?
Interpreting the SPACE Matrix involves analyzing the plotted results to determine the strategic direction of an organization. The matrix helps identify whether a company should adopt an aggressive, conservative, defensive, or competitive strategy based on its position on the matrix.
Looking for Premium maps, please visit our affiliate site: https://editablemaps.com/ or https://ofomaps.com/
Size:157K
Type: PPTX
SPACE Matrix Template
Click the link to download it.
Aspect Ratio: Standard 4:3
Click the blue button to download it.
Download the 4:3 Template
Aspect Ratio: Widescreen 16:9
Click the green button to download it.
Download the 16:9 Template
References
[1] – https://www.mbaknol.com/strategic-management/the-strategic-position-and-action-evaluation-matrix-space/
[2] – https://creately.com/guides/space-analysis/
[3] – http://businessdevelopmentadvice.com/blog/tag/space-analysis/