The Indonesia Map Template in PowerPoint format includes two slides, that is, the country map with outline and political map with provinces. Firstly, our country outline map PowerPoint templates have Indonesia capital and major cities on it. Secondly, there are 34 provinces in our Country map PowerPoint templates, in our country map template of divisions, labeling the most populated Provinces.
Indonesia is a country in Southeast Asia, known for its extensive archipelago that stretches along the equator. This strategic location has made Indonesia a key player in regional geopolitics and global trade, thanks to its pivotal position between the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Here’s a closer look at Indonesia’s location and its neighboring countries and islands.
Two slides of Indonesia map is followed.
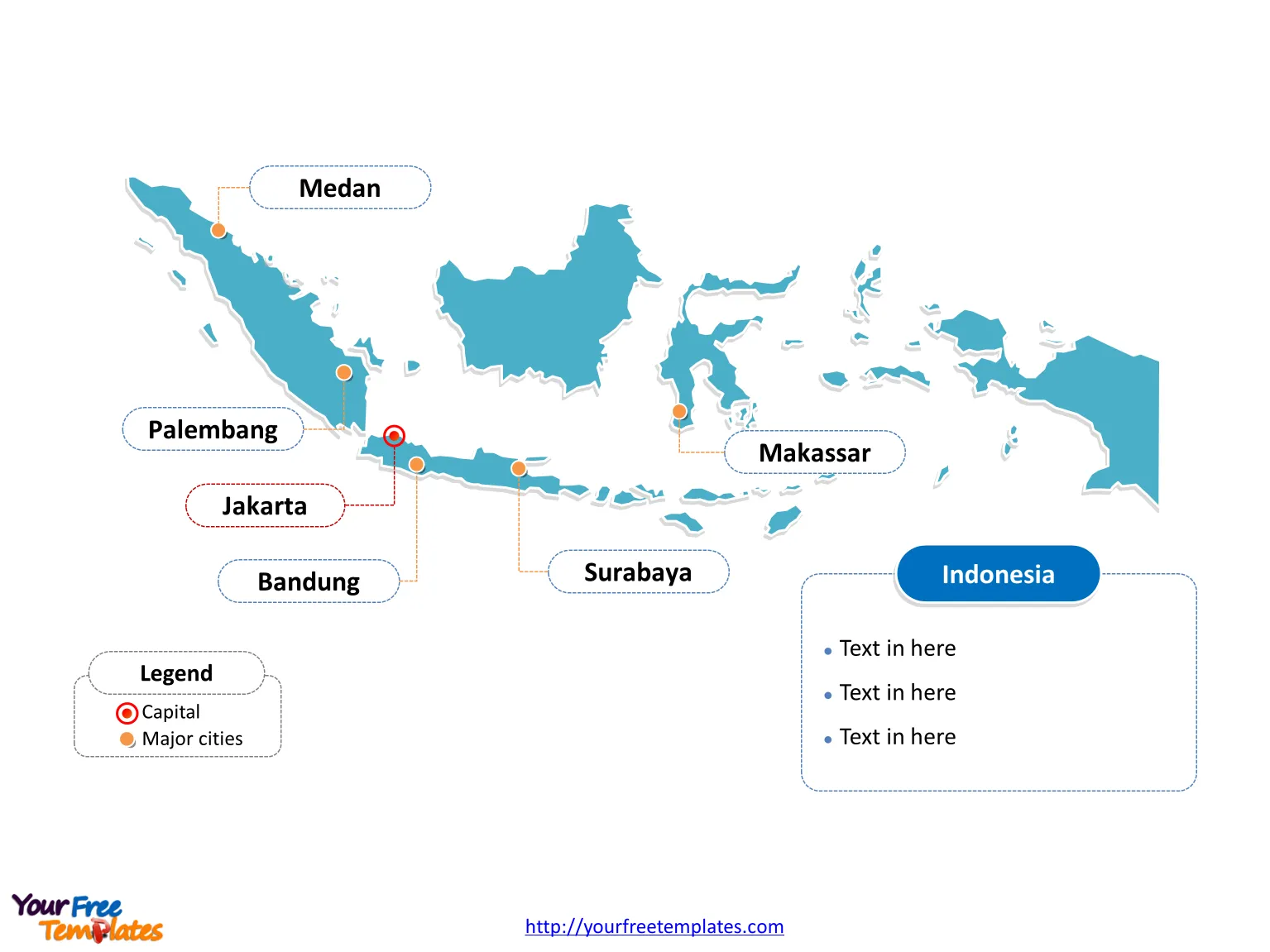
Slide 1, Map of Indonesia labeled with capital and major cities
Indonesia is situated between latitudes 11°S and 6°N, and longitudes 95°E to 141°E. The country straddles the equator, with the majority of its islands located within the tropical zone, which contributes to its diverse ecosystems and climates. Indonesia country map below shows the locations of major cities and the capital of Jakarta.
Neighboring Countries
Indonesia shares maritime borders with several countries due to its island nature. These include:
- Australia: To the south of Indonesia lies Australia, separated by the Timor Sea and Arafura Sea.
- Papua New Guinea: On the island of New Guinea, Indonesia’s province of Papua shares a land border with the independent state of Papua New Guinea to the east.
- East Timor (Timor-Leste): The island of Timor is split between Indonesia’s province of East Nusa Tenggara and the sovereign nation of East Timor.
- Malaysia:Malaysia and Indonesia share both land and maritime borders. The land border is on the island of Borneo (known as Kalimantan in Indonesia), while maritime boundaries are in the Straits of Malacca, South China Sea, and Celebes Sea.
- Singapore: North of the Indonesian islands of Batam and Bintan lies Singapore, with which Indonesia has a maritime boundary in the Straits of Singapore and Malacca.
- Philippines: To the north, across the Celebes Sea, lies the Philippines.
- Vietnam: In the South China Sea, Vietnam has maritime borders with Indonesia.
- Thailand:The maritime boundary with Thailand lies in the Andaman Sea and the Malacca Strait.
- India:Although not in direct proximity, Indonesia and India share a maritime border in the Andaman Sea.
Nearby Islands and Archipelagos
The Indonesian archipelago comprises several major island groups, including:
- Greater Sunda Islands: These include the large islands of Sumatra, Java, Borneo (shared with Malaysia and Brunei), and Sulawesi.
- Lesser Sunda Islands: This chain includes islands like Bali, Lombok, Sumbawa, Flores, Sumba, and the West Timor portion of the island of Timor.
- Maluku Islands (Moluccas): A historical spice trade hub, these islands are located between Sulawesi and Papua.
- Western New Guinea (Papua): This is the Indonesian part of the island of New Guinea, which it shares with Papua New Guinea.
Strategic Waterways
Indonesia’s waters also include significant and strategic sea lanes, such as:
- Strait of Malacca:One of the most important shipping lanes in the world, connecting the Pacific and Indian Oceans.
- Sunda Strait: Between the islands of Java and Sumatra.
- Lombok Strait: Between Bali and Lombok, it is a significant deepwater navigation channel.
You can check World map indonesia in our world map.
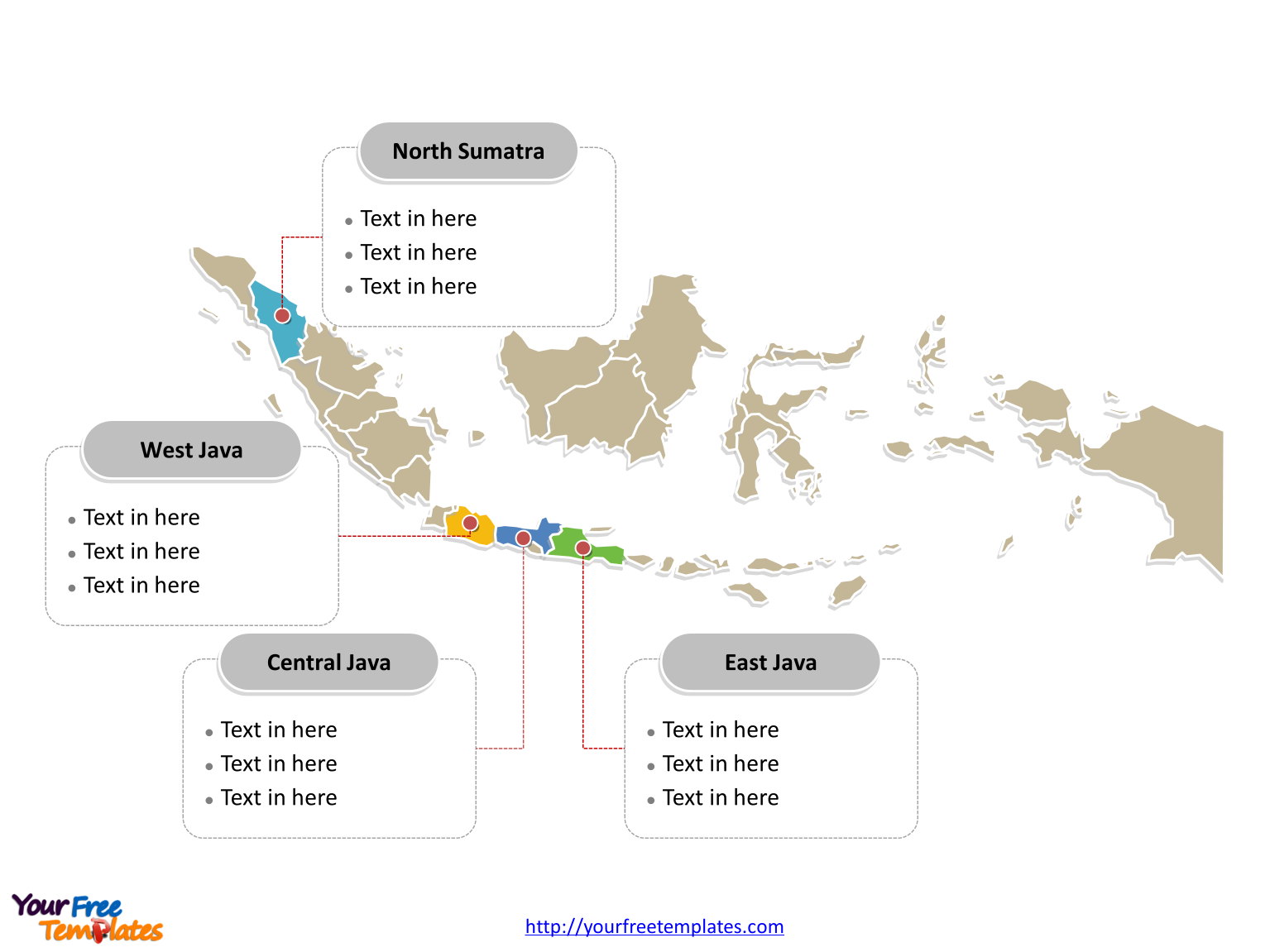
Slide 2, Indonesia Map labeled with major Provinces.
Understanding Indonesia’s Administrative Divisions
As the world’s largest archipelago, it consists of over 17,000 islands, a fact that presents unique challenges and opportunities in terms of governance and administration.
The Hierarchical Structure
Indonesia’s administrative divisions are structured in a hierarchical manner that allows for both centralized governance and regional autonomy. This structure is crucial for ensuring that each region can address its specific needs while adhering to the national policies and regulations. The main levels of this hierarchy are:
- Provinces (Provinsi):
Indonesia is divided into 34 provinces. Each province has its own local government and legislative body. The governor leads the provincial government and is elected by the residents of the province.
Firstly, there are 34 Provinces in our Indonesia map; they are Bali, Bangka–Belitung Islands, Banten, Bengkulu, Central Java, Central Kalimantan, Central Sulawesi, East Java, East Kalimantan, East Nusa Tenggara, Gorontalo, Jakarta Special Capital Region, Jambi, Lampung, Maluku, North Kalimantan, North Maluku, North Sulawesi, North Sumatra, Riau, Riau Islands, South Kalimantan, South Sulawesi, South Sumatra, Southeast Sulawesi, Special Region of Aceh, Special Region of Papua, Special Region of West Papua, Special Region of Yogyakarta, West Java, West Kalimantan, West Nusa Tenggara, West Sulawesi, West Sumatra.
- Regencies and Cities (Kabupaten and Kota):
Within provinces, there are regencies (kabupaten) and independent cities (kota). As of now, there are over 500 regencies and cities across Indonesia. Regencies are typically rural, while cities are more urbanized. Each regency and city has a regent (bupati) or a mayor (walikota) at its helm, respectively, who are also elected officials.
- Districts (Kecamatan):
Regencies and cities are further divided into districts, known as kecamatan. These are administrative units that help to manage public services at a more local level. Each district is led by a camat, who is a civil servant appointed by the regent or mayor.
- Villages and Urban Communities (Desa and Kelurahan):
- Special Regions. Indonesia also acknowledges the unique cultural and historical contexts of certain areas by granting them special status. These include:
-
- Special Capital Region of Jakarta (Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta):
As the capital city, Jakarta has a special status and is governed differently from other cities. It is the economic and political center of Indonesia.
-
- Special Region of Yogyakarta (Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta):
Yogyakarta is recognized for its traditional monarchy system and is the only province in Indonesia that is still governed by a pre-colonial sultanate.
-
- Special Region of Aceh (Daerah Istimewa Aceh):
Aceh has a degree of autonomy that allows it to implement Sharia law and has a unique administrative structure compared to other provinces.
-
- West Papua and Papua Provinces:
These provinces have special autonomy status due to their distinct cultural identity and history. They have more legislative freedom and a greater share of revenue from natural resources.
At the same time you can also refer to the fully labeled Map of Indonesia in Wikipedia.
Size: 113K
Type: PPTX
Aspect Ratio: Standard 4:3
Click the blue button to download it.
Download the 4:3 Template
Aspect Ratio: Widescreen 16:9
Click the green button to download it.
Download the 16:9 Template






![Digital Marketing: Opportunity, Strategy, and Action Digital marketing is search engine optimization (SEO), search engine marketing (SEM), content marketing, influencer marketing, content automation, campaign marketing, data-driven marketing,[8] e-commerce marketing, social media marketing, social media optimization, e-mail direct marketing, Display advertising, e–books.](https://yourfreetemplates.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/Digital_marketing_1-100x70.gif)






