Porter’s analysis stands as a cornerstone in strategic management, offering businesses a powerful tool to evaluate their competitive landscape. Developed by Michael Porter in 1979, this framework has become essential for industry analysis and shaping competitive strategy. It provides a comprehensive approach to understanding market dynamics and helps companies identify potential threats and opportunities within their sector.
At the end of this post, you can download our Porter’s Five Forces analysis PowerPoint template to fit your purpose. As the same diagram PowerPoint template series, you can also find our Competitive Strategy, National Diamond, Value Chain, Six Thinking Hats, Pareto Chart, Occam’s Razor, Data Mining, marketing segment, Porter’s five forces, SWOT Analysis, GE Matrix, BCG Matrix, Artificial Intelligence, National Diamond and BlockChain PowerPoint templates.
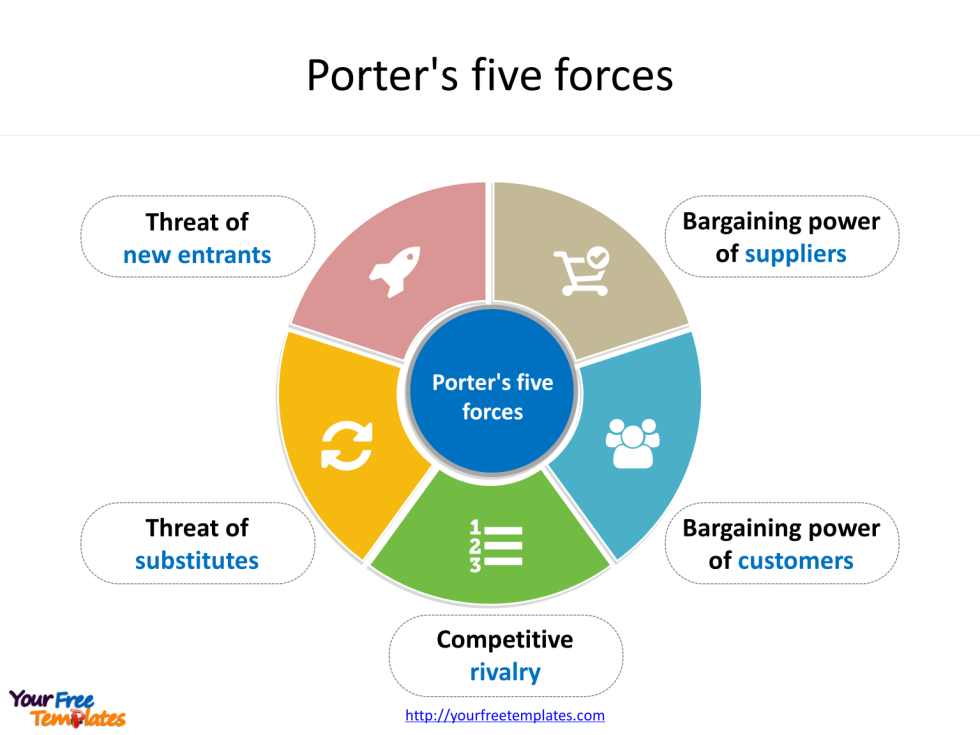
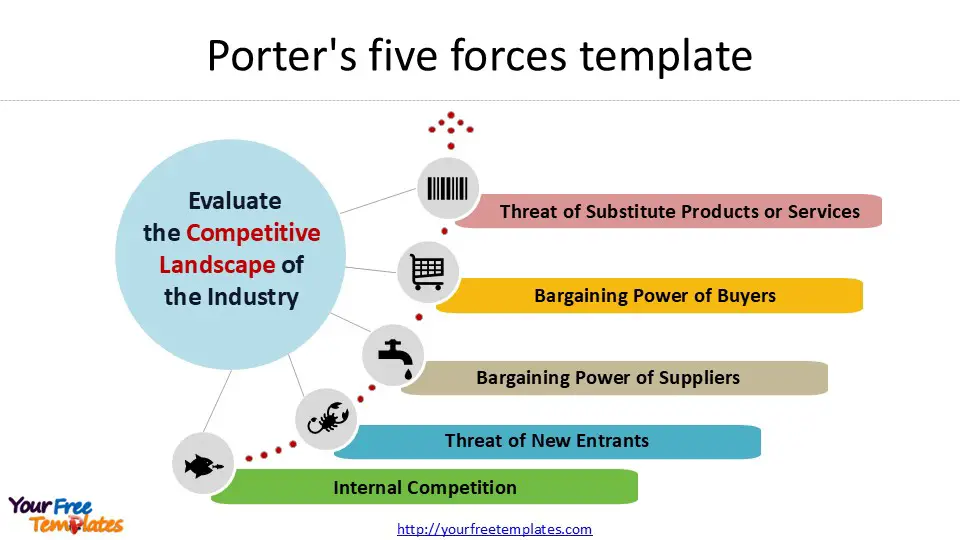
The Five Forces model examines competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, and the threat of substitute products or services. By analyzing these forces, businesses can gain valuable insights into their market position and develop strategies to enhance their competitive advantage. This strategic analysis tool has proved invaluable for companies looking to navigate complex market structures and make informed decisions about their long-term growth and sustainability.
Overview of Porter’s Five Forces Model
Origin and Purpose
Porter’s Five Forces analysis, a cornerstone in strategic management, was introduced by Michael Porter in his groundbreaking 1979 Harvard Business Review article 1 2. This framework sparked a revolution in the strategy field and continues to shape business practice and academic thinking to this day 1. The model was developed to provide a structured approach for organizations to assess their competitive environment and make informed strategic decisions 3.
The primary aim of Porter’s Five Forces model is to help businesses evaluate the competitive landscape of their industry 3. It offers a systematic method for understanding the forces that impact a company’s profitability and long-term sustainability 3. By analyzing these forces, companies can gain valuable insights into their market position and develop strategies to enhance their competitive advantage.
The Five Forces Explained
Porter’s model identifies five key forces that shape the competitive environment of an industry:
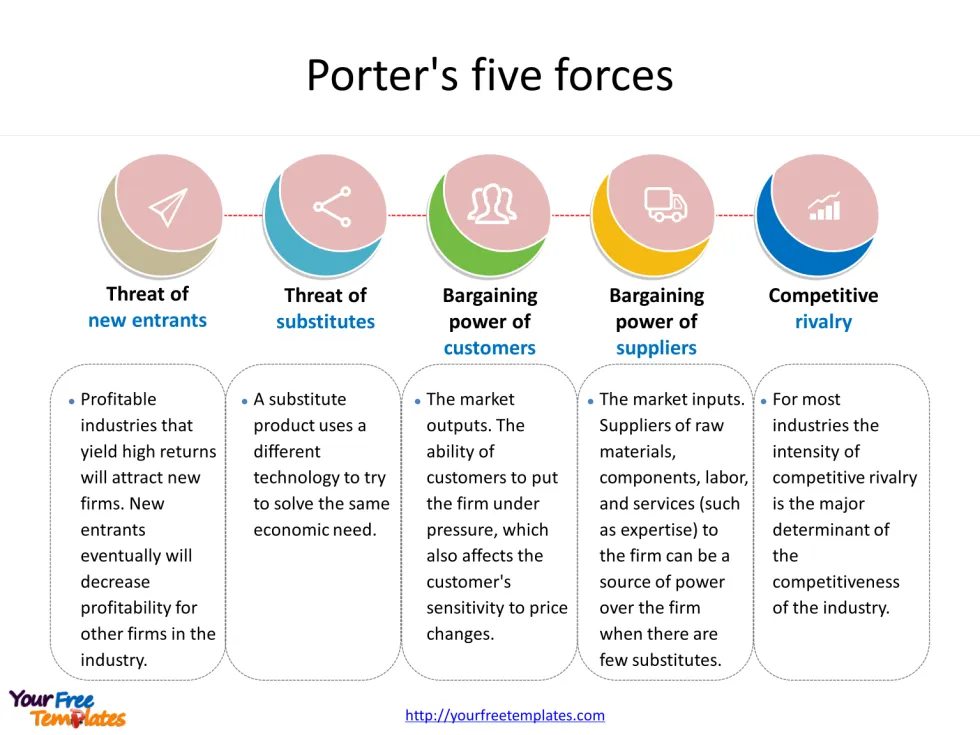
- Internal Competition: This force examines the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors within the industry.
- Threat of New Entrants: It assesses the potential for new companies to enter the market and disrupt the existing competitive landscape.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers: This force evaluates the ability of suppliers to influence prices and terms of business.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers: It analyzes the power that customers have in negotiating prices and terms.
- Threat of Substitute Products or Services: This force considers the availability of alternative products or services that could replace those offered by the industry 1 2 3.
These five forces come together in different ways for any given sector, with the intensity of competition ranging from “intense” to “mild” 2. In intensely competitive industries, all or most of the five forces have a strong influence, making it harder to achieve profits. Conversely, in “mild” industries, such as commercial aircraft manufacturing, weaker forces prevail, creating an environment more conducive to higher profits 2.
Importance in Strategic Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces analysis is essential for businesses looking to navigate complex market structures and make informed decisions about their long-term growth and sustainability. The framework provides several key benefits:
- Assessing Industry Attractiveness: The model helps companies evaluate the overall attractiveness of an industry by examining the strength of each force 1.
- Anticipating Industry Trends: By analyzing the five forces, businesses can better understand how trends will affect industry competition and prepare for future changes 1.
- Identifying Strategic Positions: The framework aids companies in finding better strategic positions within their industry, allowing them to leverage their strengths and mitigate weaknesses 1.
- Guiding Strategic Decisions: Porter’s model provides a structured approach for businesses to determine the intensity of competition and potential profitability within their market 2.
- Adapting to Market Changes: The analysis helps organizations anticipate and exploit industry structural changes, enabling them to adapt their strategies accordingly 1 3.
While Porter’s Five Forces model has faced some criticisms, such as being too static or not accounting enough for collaborative business models, it remains a fundamental tool for strategic analysts 2. The framework’s enduring relevance is evidenced by Porter’s continued work on the subject, including numerous publications expanding on the original five-force model 2.
In conclusion, Porter’s Five Forces analysis offers a timeless framework for organizations to evaluate their competitive environment, identify opportunities, and fortify their positions against threats 3. By understanding and applying this model, businesses can make more informed decisions and adapt effectively to evolving markets.
Force 1: Competitive Rivalry
Competitive rivalry, also known as industry rivalry or rivalry among existing firms, is a crucial component of Porter’s Five Forces model. This force examines the intensity of competition within an industry and its impact on profitability. Companies often engage in various tactics, such as price competition, advertising battles, and product introductions, to improve their market position 1.
Factors affecting rivalry
Several structural factors influence the intensity of industry rivalry:
- Number of competitors: When there are numerous competitors in an industry, companies may believe they can make competitive moves without being noticed 1. This can lead to increased rivalry as firms vie for market share.
- Industry growth rate: In slow-growth markets, companies can only expand by capturing market share from competitors, resulting in heightened competition 1. Conversely, in rapidly growing industries, competition may be less intense as firms can grow without directly challenging their rivals 2.
- Product differentiation: When products or services are perceived as commodities, choice is often determined by price and service, leading to increased competition in these areas 1. However, unique offerings or strong brand loyalty can reduce competitive rivalry 3.
- Fixed costs: High fixed costs create pressure for companies to fill capacity, which can lead to price cutting when there is excess capacity 1. Industries with high storage costs may also experience increased price competition as firms try to ensure sales 1.
- Exit barriers: Economic, strategic, and emotional factors can prevent companies from leaving an industry, even when they are earning low or negative returns on investments 1. This can result in prolonged periods of intense competition.
Examples of intense rivalry
Intense rivalries are common across various industries, often leading to fierce competition and innovative strategies. Some notable examples include:
- Soft drinks: Pepsi and Coca-Cola have a long-standing rivalry that has shaped the beverage industry 3.
- Smartphones: Apple and Samsung compete intensely in the smartphone market, driving technological advancements and marketing innovations 3.
- Sportswear: Nike and Adidas engage in ongoing competition, influencing trends in athletic apparel and footwear 3.
- Automobiles: Ford and General Motors have a historic rivalry that has impacted the automotive industry for decades 3.
- Streaming services: Netflix and Hulu compete for subscribers in the rapidly evolving streaming market 3.
These rivalries often result in price wars, high-priced marketing battles, and races for slight advances that could provide a competitive edge 3. While such competition can stimulate innovation and product improvements, it can also erode profits and market stability 3.
Strategies to address rivalry
To navigate intense competitive environments, companies can employ various strategies:
- Differentiation: Offering unique products or services can help a company stand out from competitors and reduce price-based competition 3. For example, Apple has successfully differentiated itself through its ecosystem of products and services.
- Cost leadership: Becoming the low-cost producer in an industry can provide a competitive advantage, especially in markets where price is a significant factor 1.
- Focus on strengths: Companies can concentrate on promoting their own strengths rather than directly attacking competitors 4. This approach can help maintain a positive brand image while still addressing competitive pressures.
- Innovation: Continuously improving products or services can help a company stay ahead of competitors and maintain market share 3.
- Strategic partnerships: Forming alliances with other companies can help firms access new resources, technologies, or markets, potentially reducing competitive pressures 1.
- Market expansion: Exploring global opportunities or entering new market segments can help companies reduce their dependence on highly competitive markets 2.
By understanding the factors that influence competitive rivalry and implementing appropriate strategies, companies can better position themselves to succeed in challenging competitive landscapes. Effective management of this force is crucial for maintaining profitability and long-term success in any industry.
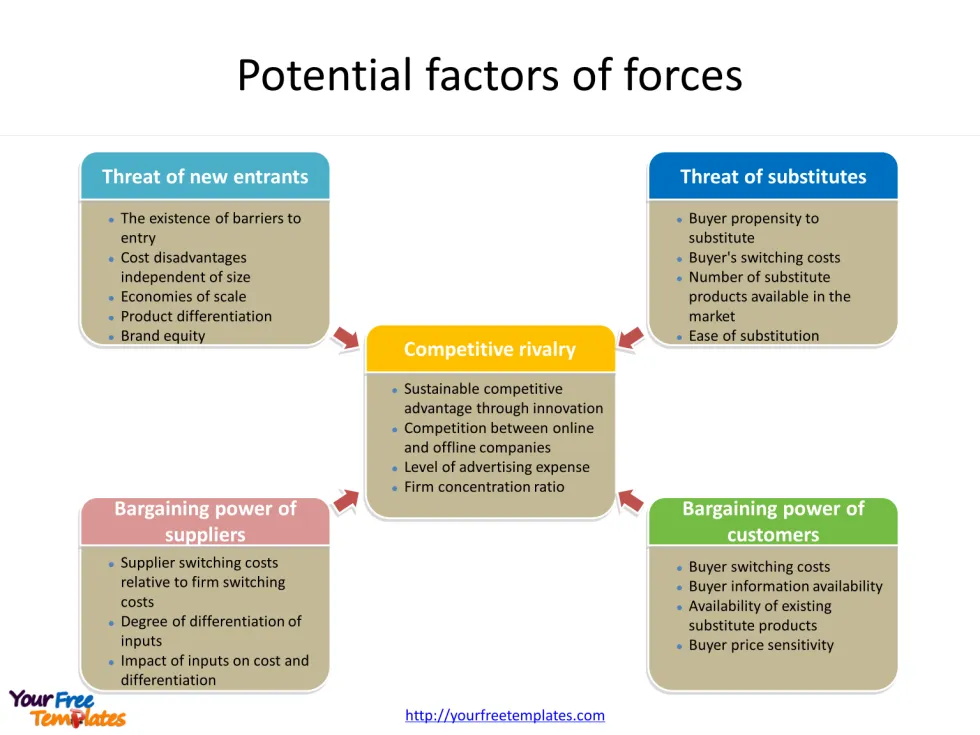
Force 2: Threat of New Entrants
The threat of new entrants is a crucial component of Porter’s Five Forces industry analysis framework. It refers to the potential for new competitors to enter an industry and challenge existing players 1. This force has a significant impact on the profitability of current companies within the sector 1.
Entry Barriers
The intensity of the threat posed by new entrants largely depends on the barriers to entry present in the industry 1. These barriers are obstacles or high costs that can deter new competitors from entering the market 1. Several factors contribute to creating entry barriers:
- Brand Loyalty: When customers show a strong preference for products or services offered by existing companies, it becomes challenging for new entrants to gain market share 1.
- Cost Advantages: Established firms may have the ability to produce and offer their products or services at lower costs compared to potential new entrants 1.
- Capital Requirements: Some industries require substantial initial investments, such as in telecommunications, which can discourage new competitors 1.
- Access to Suppliers and Distribution Channels: Existing companies may have exclusive rights to suppliers and distribution networks, making it difficult for newcomers to establish themselves 1.
- Retaliation: Incumbent firms may collaborate to deter new entrants through various strategies 1.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Government regulations and licensing requirements can create significant barriers for new companies 2.
- Economies of Scale: As production volume increases, unit costs may decrease, forcing new entrants to either enter at a large scale or face a cost disadvantage 3.
Impact on Industry Profitability
The level of threat posed by new entrants has a direct influence on the attractiveness and profitability of an industry:
- Low Threat of New Entrants: When entry barriers are high, the industry becomes more attractive to existing players. This situation allows incumbent firms to potentially enjoy increased profits due to reduced competition 1.
- High Threat of New Entrants: Conversely, when entry barriers are low, the industry becomes less attractive. New competitors can easily enter the market, compete with existing firms, and capture market share. This scenario often leads to reduced profit potential as more players vie for the same customer base 1.
Ways to Deter New Entrants
Established companies employ various strategies to discourage new entrants and maintain their market positions:
- Leveraging Economies of Scale: By operating at a large scale, incumbent firms can achieve cost advantages that are difficult for new entrants to match 3.
- Building Strong Brand Identity: Developing customer loyalty and brand recognition creates a significant hurdle for newcomers 2.
- Investing in Research and Development: Continuous innovation can help maintain a technological edge over potential new entrants 2.
- Controlling Key Resources: Securing exclusive access to essential suppliers or distribution channels can limit opportunities for new competitors 1.
- Lobbying for Regulatory Protection: In some cases, established firms may influence government policies to create or maintain barriers to entry 2.
- Aggressive Marketing and Pricing Strategies: Incumbents may increase advertising spending or engage in price competition to make market entry less attractive 3.
- Creating High Switching Costs: By developing products or services that are costly for customers to switch away from, companies can deter new entrants 2.
Understanding and managing the threat of new entrants is crucial for businesses looking to maintain their competitive advantage. By analyzing this force, companies can better position themselves to defend against potential newcomers and sustain their profitability in the long term.
Force 3: Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers is a crucial component of Porter’s Five Forces Industry Analysis Framework. This force refers to the ability of suppliers to exert pressure on companies by raising prices, lowering product quality, or reducing product availability 1. It plays a significant role in shaping the competitive landscape of an industry and determining its overall attractiveness 2.
Factors influencing supplier power
Several key factors contribute to the strength or weakness of supplier bargaining power:
- Number of suppliers: When there are fewer suppliers relative to buyers, supplier power tends to be higher 3.
- Supplier dependency: If a supplier’s sales are not heavily dependent on a particular buyer, their bargaining power increases 3.
- Switching costs: High switching costs for buyers strengthen supplier power, while low switching costs for suppliers themselves also enhance their position 3.
- Product differentiation: Unique or highly differentiated products give suppliers more leverage 1.
- Threat of forward integration: When suppliers can potentially integrate forward into the buyer’s industry, their bargaining power increases 3.
- Availability of substitutes: The lack of substitute products strengthens supplier power 3.
- Industry importance: If the supplier’s industry is more crucial to the buyer than vice versa, supplier power is enhanced 1.
Effects on businesses
The bargaining power of suppliers can significantly impact businesses in several ways:
- Profitability: Strong supplier power can reduce profit potential in an industry by increasing costs or reducing product quality 1.
- Price sensitivity: In industries with high price sensitivity, powerful suppliers can significantly affect buyer profitability 2.
- Contract terms: When supplier power is high, contract and invoice terms may be less favorable for buyers 2.
- Supply chain volatility: Strong supplier power can lead to increased volatility in the supply chain, affecting business operations 1.
- Product quality: Powerful suppliers may have the ability to influence product quality, potentially impacting the buyer’s end product 1.
- Market dynamics: The relative strength of supplier power can affect overall market dynamics and competition within an industry 2.
Strategies to manage supplier power
Businesses can employ various strategies to manage and mitigate the bargaining power of suppliers:
- Diversification of supply chain: By diversifying their supply chain, companies can reduce reliance on a single supplier and enhance resilience to disruptions 1.
- Use of substitutes: Exploring and utilizing substitute raw materials or products can help reduce dependency on powerful suppliers 1.
- Backward integration: Companies may consider producing key supplies themselves to eliminate supplier bargaining power 1. For example, Apple has begun developing its own processors to reduce reliance on powerful vendors like AMD and Intel 1.
- Strategic partnerships: Negotiating exclusivity agreements or forming strategic partnerships with suppliers can help control their bargaining power 1.
- Centralized procurement: Establishing a central procurement unit can consolidate orders and strengthen negotiating power with suppliers 1.
- Market expansion: Offering suppliers new market opportunities in exchange for price concessions can help gain an upper hand in negotiations 1.
- Private label products: Retail companies may develop their own private label products to compete with supplier brands and maintain control over pricing 1.
- Automation tools: Implementing automation software for purchase order management, supplier relationship management, and spend management can improve efficiency and control in dealing with suppliers 2.
By carefully analyzing the factors influencing supplier power and implementing appropriate strategies, businesses can effectively manage this force and improve their competitive position within their industry.
Force 4: Bargaining Power of Buyers
The bargaining power of buyers is a crucial component of Porter’s Five Forces industry analysis framework. It refers to the ability of customers to exert pressure on businesses, influencing factors such as product prices, quality, and service levels 1. This force plays a significant role in shaping the competitive landscape and determining the overall attractiveness of an industry 1.
Determinants of buyer power
Several factors contribute to the strength of buyer bargaining power:
- Number of buyers relative to suppliers: When there are fewer buyers compared to suppliers, buyer power tends to be stronger 3.
- Dependence on specific suppliers: If buyers can easily obtain similar products or services from multiple suppliers, their bargaining power increases 3.
- Switching costs: Low switching costs for buyers enhance their bargaining position, while high switching costs reduce it 3.
- Purchase volume: Buyers who purchase products in bulk often have greater leverage in negotiations 3.
- Product differentiation: When products are not highly differentiated, buyers have more options and, consequently, more power 3.
- Availability of substitutes: The presence of numerous substitute products in the market strengthens buyer bargaining power 3.
- Backward integration potential: If buyers can potentially integrate backward into the supplier’s industry, their bargaining power increases 3.
Consequences for businesses
The bargaining power of buyers can significantly impact businesses in several ways:
- Profitability: Strong buyer power can reduce profit potential in an industry by forcing down prices or demanding higher quality and better service 1.
- Price sensitivity: In industries with high price sensitivity, powerful buyers can significantly affect seller profitability 2.
- Competitive pressure: Buyers can increase competition within an industry by playing competitors against one another 1.
- Contract terms: When buyer power is high, contract and invoice terms may be less favorable for sellers 2.
- Product quality: Powerful buyers may demand higher quality products or services without corresponding price increases 1.
- Industry dynamics: The relative strength of buyer power can affect overall market dynamics and competition within an industry 2.
Tactics to reduce buyer power
Businesses can employ various strategies to mitigate the bargaining power of buyers:
- Increase switching costs: Companies can create an environment that makes buyers more reliant on their products or services. Apple’s “ecosystem” is an excellent example of this strategy, where interconnected products and services make it difficult for customers to switch to competitors 1.
- Vertical integration: Exploring forward vertical integration opportunities can help businesses bypass intermediaries and gain direct access to consumers. For instance, Nike’s introduction of retail stores as a Direct-to-Consumer sales strategy allowed them to dictate their terms and project an exclusive brand identity 1.
- Offer differentiated value: When products are comparable, differentiation can involve pricing, value features, performance, efficacy, durability, or warranty. This approach is particularly relevant in consumer markets 1.
- Develop innovative business models: Companies with novel technologies can consider licensing rather than selling, limiting customer access to technological know-how and creating new revenue streams through installation and after-sales support 1.
- Personalize customer experience: Tailoring product interactions and engaging with customers as individuals can make it more difficult for them to switch to competitors. Amazon’s AI-driven product recommendations exemplify this approach, improving the overall shopping experience 1.
- Implement strategic pricing and offers: Lowering product prices, offering discounts on long-term memberships, and providing free product upgrades are conventional ways to retain customers and reduce their bargaining power 1.
By understanding and addressing the factors that influence buyer bargaining power, businesses can better position themselves to maintain profitability and competitiveness in their respective industries.
Conclusion
Porter’s Five Forces analysis offers businesses a powerful tool to size up their competitive landscape. This framework has a significant impact on strategic management, helping companies identify potential threats and opportunities within their sector. By examining competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, and the threat of substitutes, businesses can gain valuable insights into their market position and develop strategies to enhance their competitive advantage.
This strategic analysis tool has proven invaluable for companies looking to navigate complex market structures and make informed decisions about their long-term growth and sustainability. It provides a structured approach to understand market dynamics and helps businesses adapt to evolving markets effectively. In the end, Porter’s Five Forces analysis remains a timeless framework for organizations to evaluate their competitive environment, spot opportunities, and strengthen their positions against threats.
FAQs
1. What are the practical uses of Porter’s Five Forces?
Porter’s Five Forces framework is utilized to assess and understand the competitive dynamics within an industry. This includes analyzing existing competitive rivalries, the threat posed by new market entrants, the negotiation strength of suppliers, the bargaining power of customers, and the threat of substitute products or services.
2. How does Porter’s Five Forces model apply to marketing strategies?
The Five Forces model by Porter helps organizations to broaden their competitive analysis beyond immediate rivals. This includes examining competitive rivalry, supplier influence, buyer power, the risk of substitute products or services, and the threat of new entrants. This comprehensive view aids in strategic decision-making in marketing.
3. Why is the Five Forces model valuable for industry analysis?
The Five Forces model is crucial for understanding how competitive forces shape the profitability and attractiveness of an industry. It aids businesses in predicting changes in competition, understanding how the structure of the industry is evolving, and identifying advantageous strategic positions.
4. How can one effectively implement Porter’s Five Forces analysis?
To effectively use Porter’s Five Forces, begin by analyzing the intensity of competition within your industry. Next, assess the bargaining power of your suppliers and buyers. Identify any potential threats from new entrants into the market. Finally, consider the threat posed by substitute products or services. This comprehensive evaluation helps in crafting robust business strategies.
Need premium maps, pls visit our map shop: https://editablemaps.com
Size:150K
Type: PPTX
Porter’s five forces Template
Click the link to download it.
Aspect Ratio: Standard 4:3
Click the blue button to download Porter’s five forces template.
Download the 4:3 Template
Aspect Ratio: Widescreen 16:9
Click the green button to download Porter’s five forces template.
Download the 16:9 Template
References
[1] – https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/porter.asp
[2] – https://getlucidity.com/strategy-resources/introduction-to-porters-five-forces/
[3] – https://www.forbes.com/advisor/business/porters-five-forces/
[4] – https://getlucidity.com/strategy-resources/guide-to-five-forces/